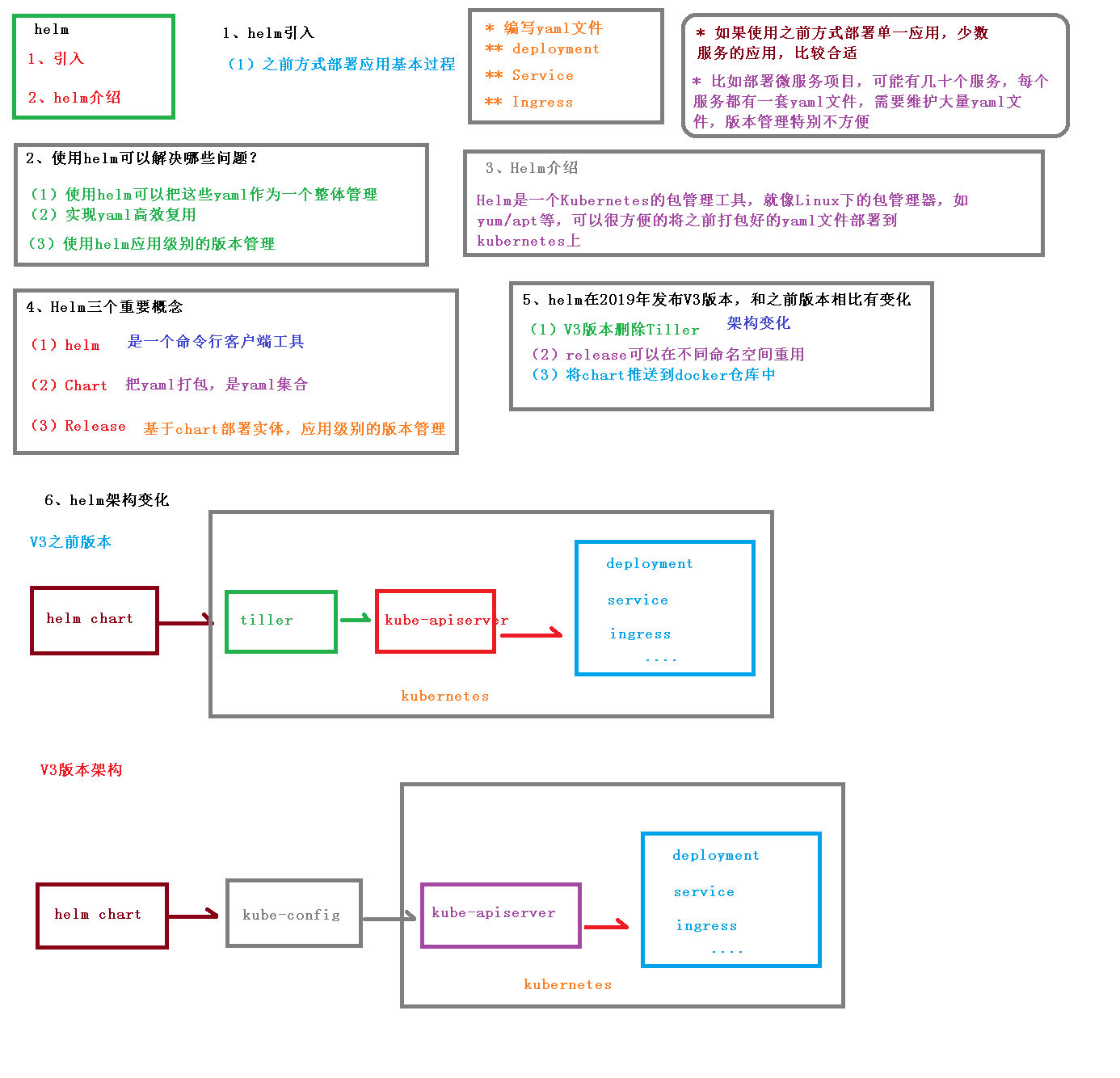
K8S
k8s是一组服务器集群
Google2014年开业的容器化集群管理系统
k8s管理集群节点上的容器
Docker Swarm 2019-07 阿里云宣布 Docker Swarm 剔除
Kubernetes Google 10年容器化基础架构 borg GO 语言 Borg
特点:
轻量级:消耗资源小
开源
弹性伸缩
负载均衡:IPVS
功能:
- 自我修复
- 弹性伸缩:实时根据服务器的并发情况增加或缩减容器数量
- 自动部署
- 回滚
- 负载均衡和服务发现
- 机密和配置管理
- 存储编排
- 批处理
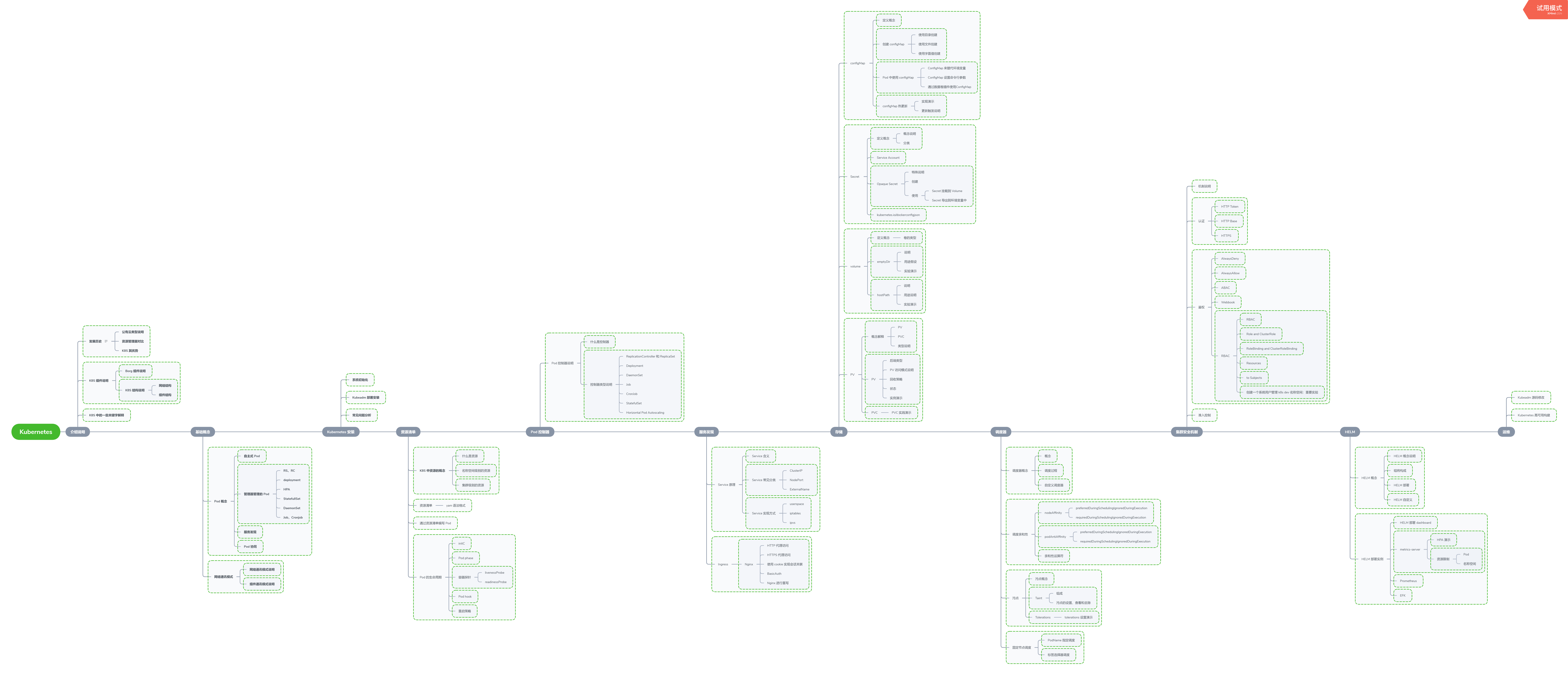
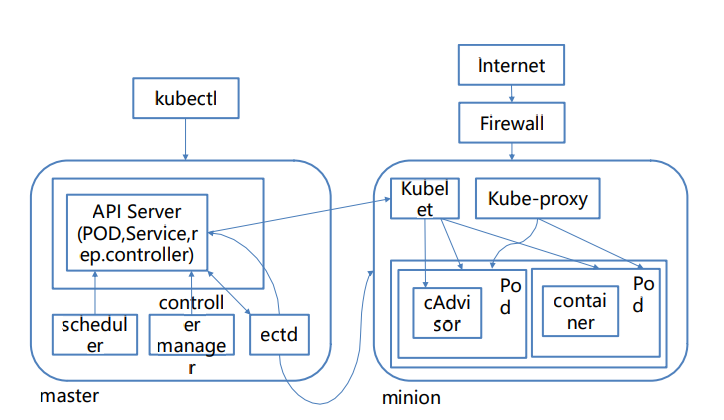
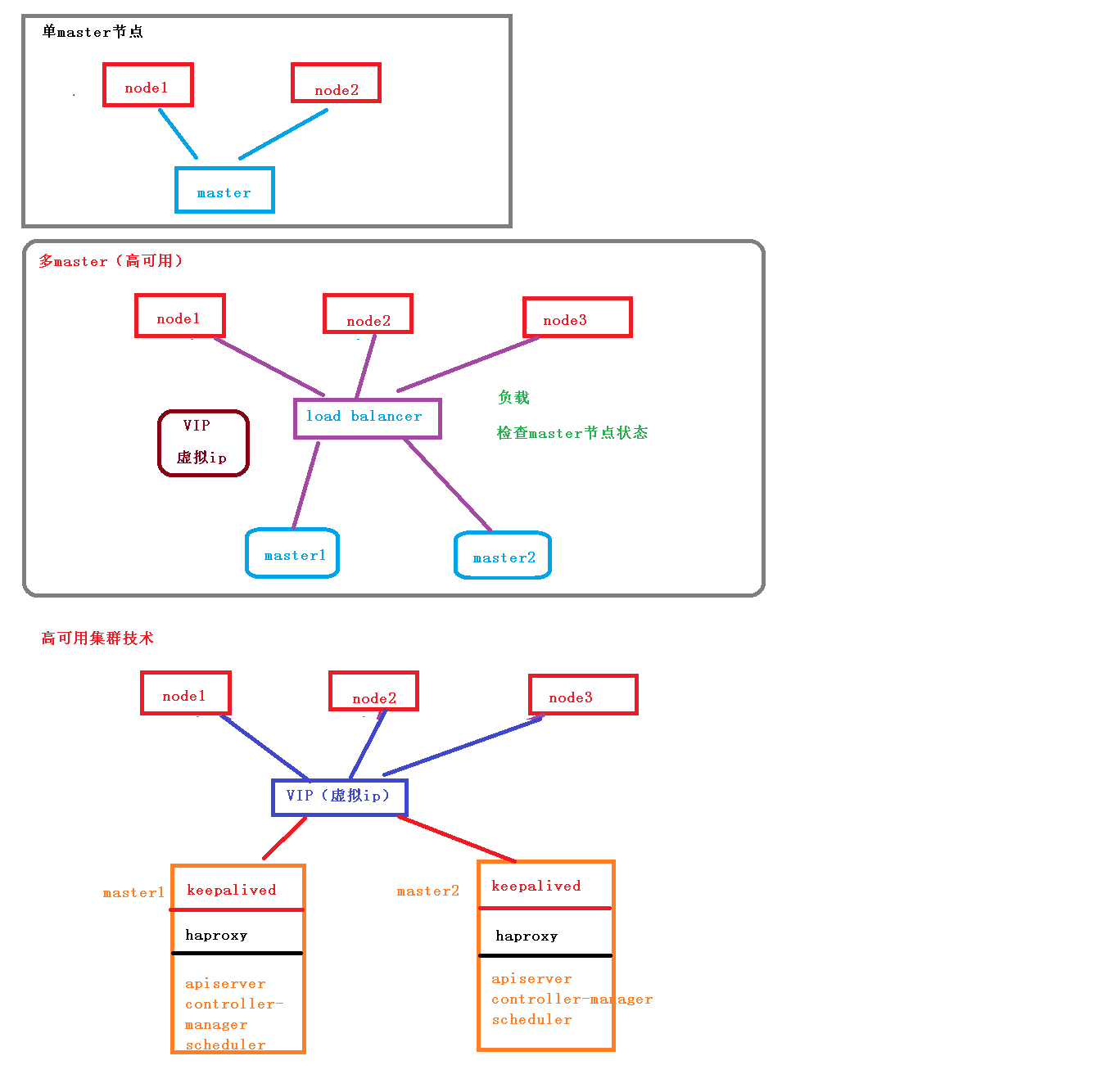
k8s集群分为两类节点
master node:主
worker node:工作
master节点的组件:
- apiserver:接收客户端操作k8s的指令,所有访问的统一入口
- schduler:从多个work node节点选一个来启动服务(可生成缓存,并不是都要apiserver处理)
- controller manager:向worker节点的kubelet发送指令
node节点组件(程序)
- kubelet:向docker发送指令管理docker容器,维持pod生命周期
- kubeproxy:管理docker容器的网络
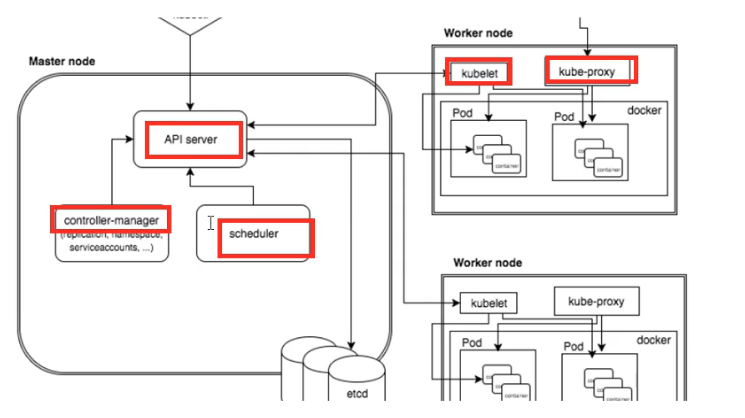
ectd:(HTTP Server 因为http天生支持put get change 等,不需要开发PCP流程)
可信赖的分布式键值存储服务,扩容方便
k8s数据库,用来注册节点、服务、记录账户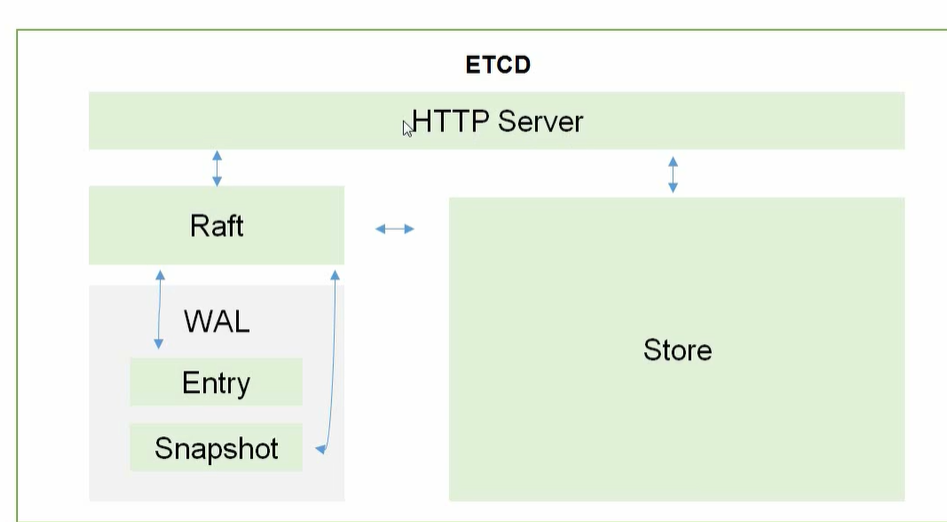
Raft:读写操作
WAL:预写日志
store:实时把数据写入
POD(自主式pod-自生自灭,控制器管理的pod)
- 最小部署单元
- 一组容器集和
- 一个pod中的容器共享网络命名空间
- pod短暂
一个POD里有pause,共享网络和数据卷volumes,因此localhost就可以访问,容器间的端口不能冲突K8S里不能直接启动容器
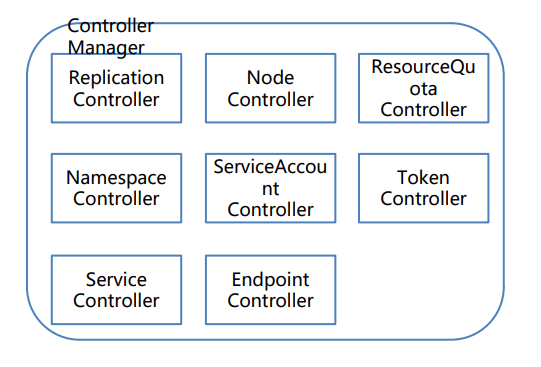
Controllers
- ReplicaSet(RS):确保预期的Pod副本数量,支持selector(创建pod时会打标签,当需要批量处理时可以用)
- Development:无状态应用部署(管理RS,防止不兼容,docker面对无状态服务,没有存储需要实时的保留,比如apache)
StatefulSet:有状态应用部署(有状态服务mogodb mysql,需要实时的数据更新和存储,抽离出集群再放回去就没办法正常工作了)
- 稳定的持久化存储,即POD重新调度后还能访问到相同的持久化数据,基于PVC实现
- 稳定的网络标志,即POD重新调度后其PodName和HostName不变,基于Headless Service(没有Cluster IP的Service)
- 有序部署有序回收(下一个POD运行前,之前的POD都是Running和Ready状态)
- DaemonSet:确保所有(或一些)Node运行同一个Pod
- Job:一次性任务
- Cronjob:定时任务
- HPA(HorizontalPodAutoScale):自动扩容,仅适用于Development和ReplicaSet
Service:关联一组pod,提供统一入口,即使pod地址发生改变,这个统一地址也不会改变
Label:标签,一组pod有一个统一的标签,service通过label和一组pod关联
NameSpace:名称空间
- 【默认pod可以互相访问】
- 为不同公司提供隔离pod使用场景
- 测试、开发、上线环境的pod
COREDNS:可以为集群中的SVC创建一个域名IP的对应关系解析
DASHBOARD:给 K8S 集群提供一个 B/S 结构访问体系
INGRESS CONTROLLER:官方只能实现四层代理,INGRESS 可以实现七层代理
FEDERATION:提供一个可以跨集群中心多K8S统一管理功能
PROMETHEUS:提供K8S集群的监控能力
ELK:提供 K8S 集群日志统一分析介入平台

POD可以直接访问,一个网段,Overlay Network
Pod与Service之间:各节点的iptables规则
POD里的container是不同端口,他们共享PAUSE网络站,通过localhost就可以访问
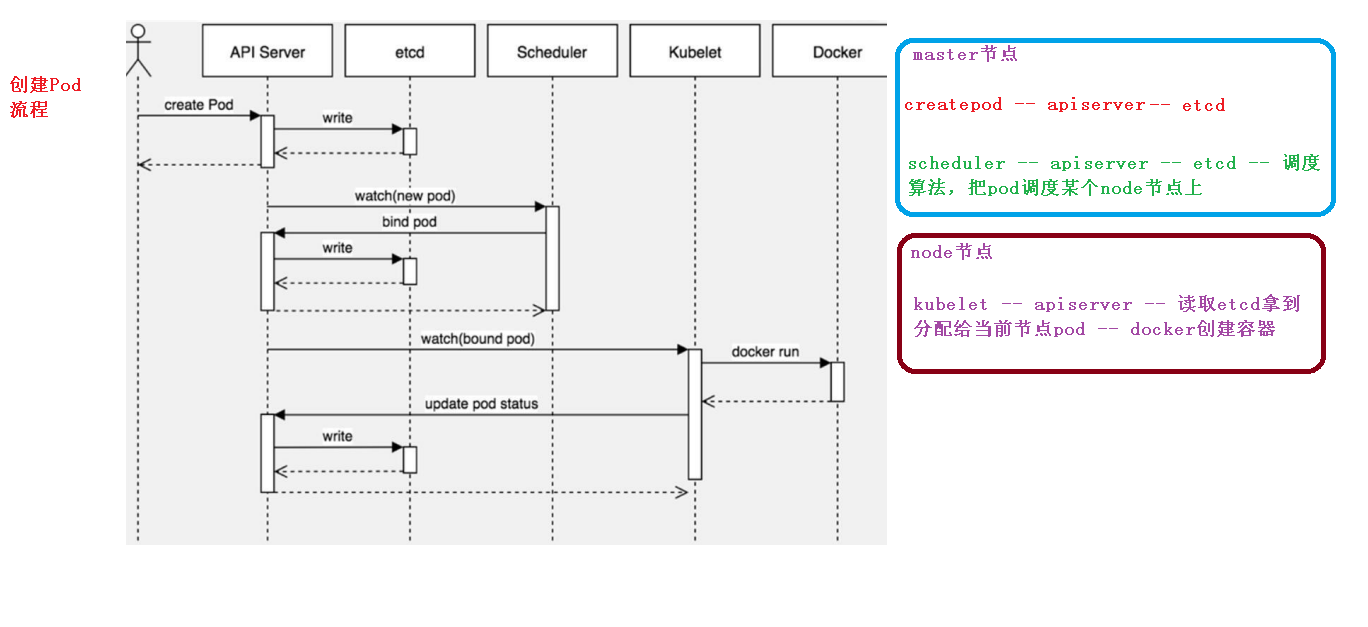
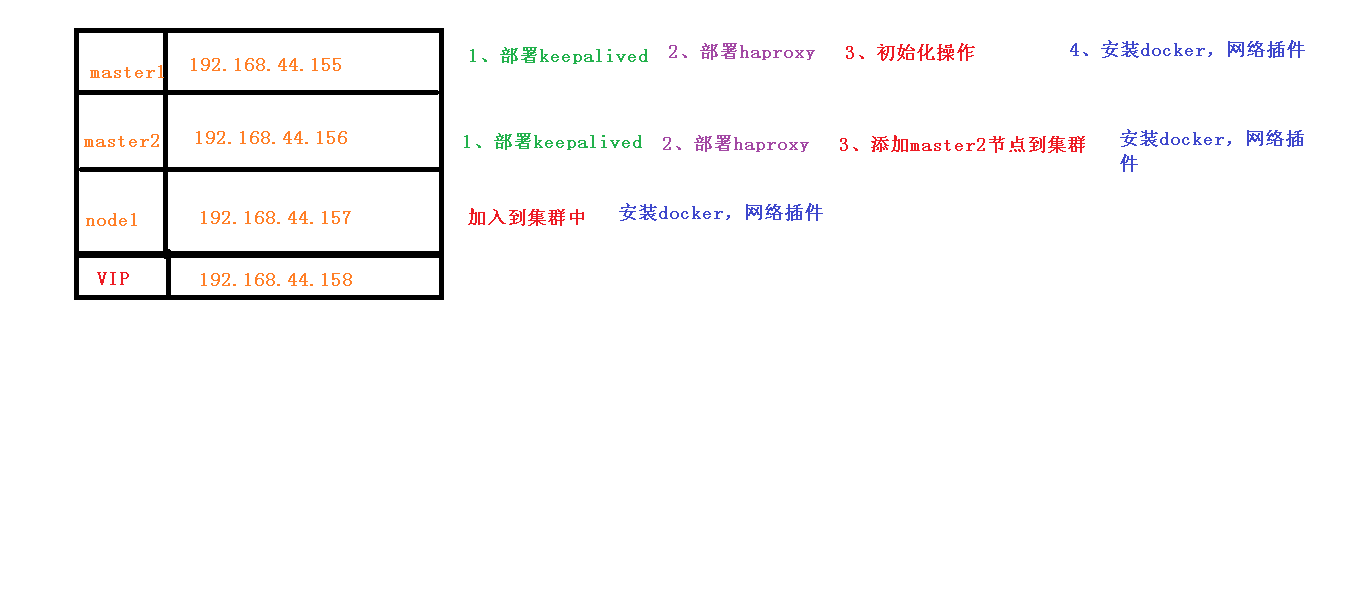
### 搭建k8s集群步骤
Pod
创建和管理的最小单元,用户创建或部署的最小资源对象模型
运行容器化应用的资源对象。其他资源对象都是用来支撑或扩展Pod功能的
Pod共享网络命名空间
Pod短暂
Pod存在的意义
(1)创建容器使用docker,一个docker对应一个容器,一个容器有进程,一个容器运行一个应用程序
(2)Pod多进程,运行多个应用程序
* 一个Pod有多个容器,一个容器里运行一个应用程序
(3)Pod为了亲密性应用
* 应用之间进行交互
* 网络之间调用
* 两个应用需要频繁调用Pod实现机制
(1)共享网络:通过Pause容器,把其他业务容器加入到Pause容器里面,公用一个namespace
(2)共享存储:数据卷volumn
pod 持久化数据(日志数据,业务数据)
Pod镜像拉取策略:imagePullPolicy
* Always:总是拉取 pull
* IfNotPresent:默认值,本地有则使用本地镜像,不拉取
* Never:只使用本地镜像,从不拉取
Pod资源限制
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: mysql
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: mysql
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: mysql
spec:
containers:
- image: mysql
name: mysql
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests: #调度
memory: "64Mi"
cpu: "250m"
limits: # 最大
memory: "128Mi"
cpu: "500m"Pod重启机制
restartPolicy:Never | Always|onFailure
Never:容器终止退出后,从不重启容器
onFailure: 异常退出(状态码为非0)才重启
Always: 默认策略,总是重启容器
Pod健康检查
livenessProbe(存活检查)检查失败,杀死容器,根据Pod的restartPolicy来操作
readinessProbe(就绪检查)检查失败,从service endpoints中剔除Pod
探测方式包括:
- HTTP:200-400成功
- TCP:tcpsocket建立成功
- Exec命令:返回状态码是0成功

调度策略
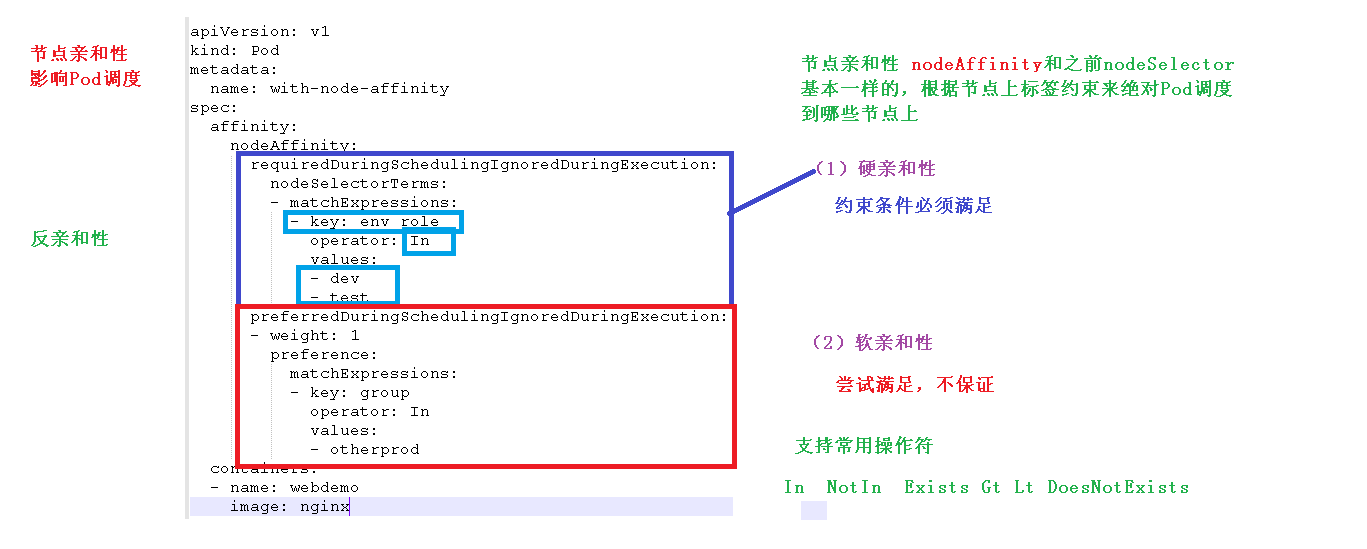
节点亲和性
nodeAffinity和之前nodeSelector基本一样,根据节点上标签约束来绝对Pod调度到哪些节点上
硬策略(required):必须满足,不满足则Pod处于Pending状态
软策略(preferred):尝试满足,但不保证
这里的匹配逻辑是label在某个列表中,可选的操作符有:
In: label的值在某个列表中
NotIn:label的值不在某个列表中
Exists:某个label存在
DoesNotExist:某个label不存在
Gt:label的值大于某个值(字符串比较)
Lt:label的值小于某个值(字符串比较)
如果nodeAffinity中nodeSelector有多个选项,节点满足任何一个条件即可;如果matchExpressions有多个选项,则节点必须同时满足这些选项才能运行pod 。
污点和污点容忍
node打上污点(可以想象成一个标签),pod如果不定义容忍这个污点,那么pod就不会被调度器分配到这个node
kubectl taint nodes node1 key=value:NoSchedule
kubectl taint nodes node1 key=value:NoExecute
kubectl taint nodes node1 key=value:PreferNoSchedule
NoSchedule:K新的不能容忍的pod不能再调度过来,但是老的运行在node上不受影响
NoExecute:新的不能容忍的pod不能调度过来,老的pod也会被驱逐
PreferNoSchedule:pod会尝试将pod分配到该节点
删除污点
kubectl taint nodes kube11 key:NoSchedule-
pod设置容忍一个污点
tolerations: #containers同级
- key: "key1" #能容忍的污点key
operator: "Equal" #Equal等于表示key=value , Exists不等于,表示当值不等于下面value正常
value: "value1" #值
effect: "NoExecute" #effect策略,见上面
tolerationSeconds: 3600 #原始的pod多久驱逐,注意只有effect: "NoExecute"才能设置,不然报错
deployment添加容忍这个污点
apiVersion: apps/v1Beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deploy
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
images: nginx:laste
ports:
- containerPort: 80
tolerations:
- key: "disktype"
operator: "Equal"
value: "value1"
effect: "NoExecute"
tolerationSeconds: 3600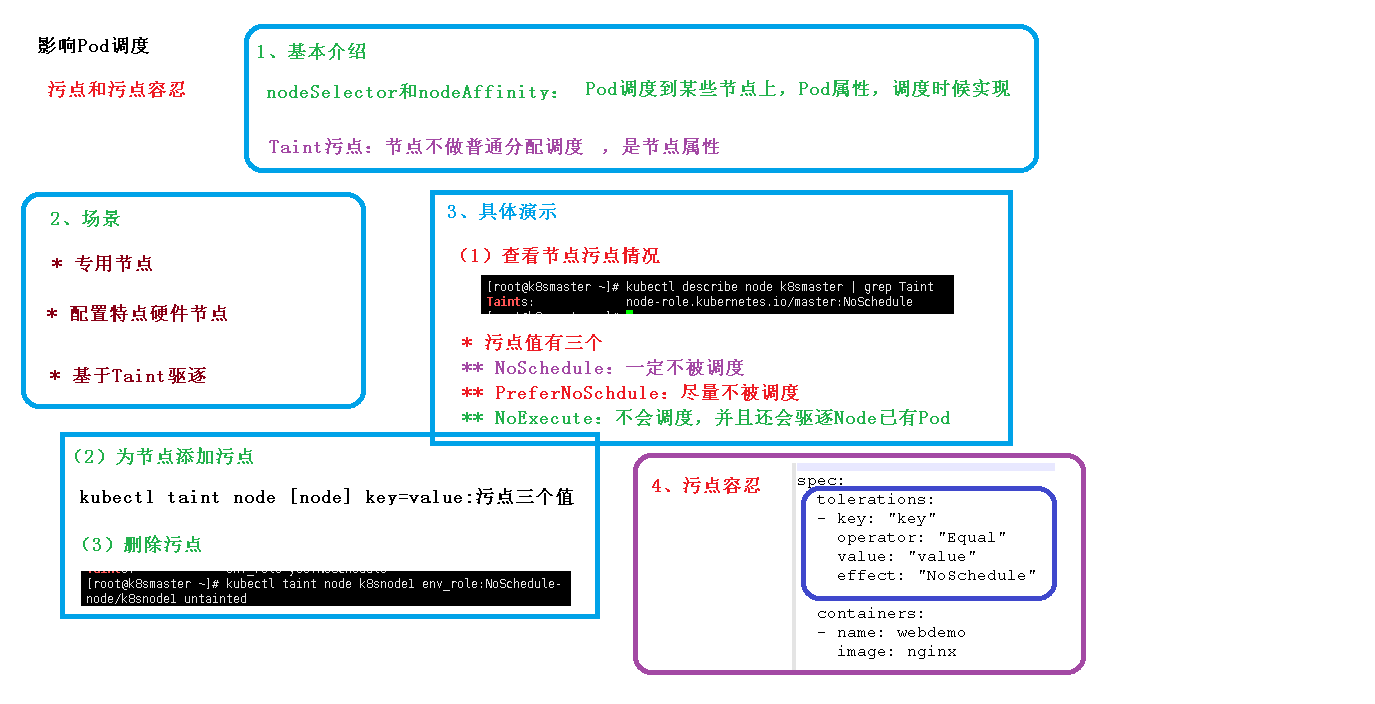
controller
在集群上管理和运行容器对象
POD和controller关系(Label标签)
pod通过controller实现应用的运维,比如伸缩、滚动升级(新建一个新的,kill一个旧的)等
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-f89759699-m84dg 1/1 Running 0 6m26s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-f89759699-m84dg 1/1 Running 0 6m32s 10.244.2.13 k8s-node1 <none> <none>
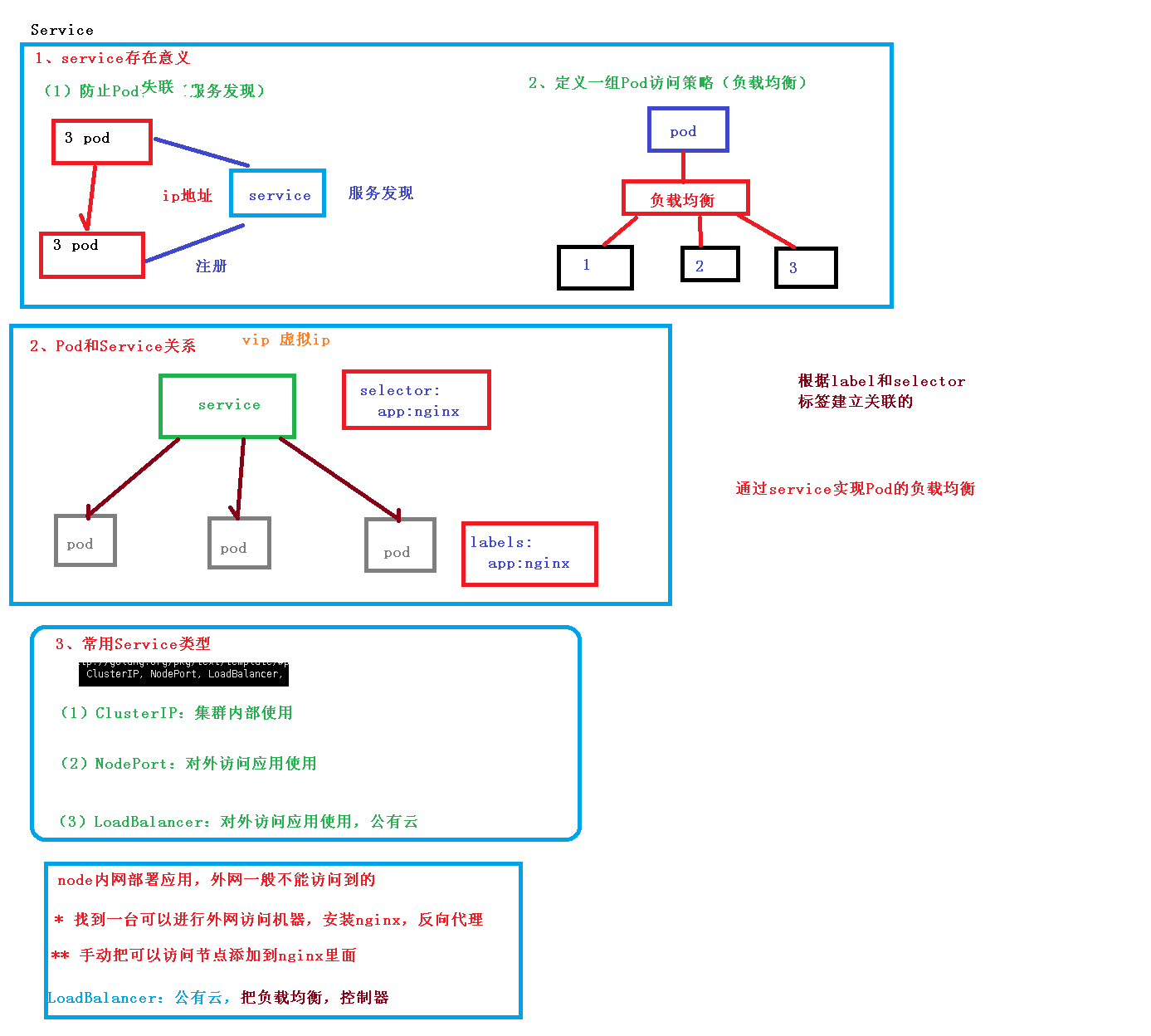
SERVICE
Service是一种抽象的对象
服务发现和负载均衡
一个Serivce下面包含的Pod集合一般是由Label Selector来决定的。
三种IP
Node IP:Node节点的IP地址:Node IP是Kubernetes集群中节点的物理网卡IP地址(一般为内网),所有属于这个网络的服务器之间都可以直接通信,所以Kubernetes集群外要想访问Kubernetes集群内部的某个节点或者服务,肯定得通过Node IP进行通信(这个时候一般是通过外网IP了)
Pod IP:Pod的IP地址:每个Pod的IP地址,它是Docker Engine根据docker0网桥的IP地址段进行分配的
Cluster IP:Service的IP地址:虚拟的IP,仅仅作用于Kubernetes Service这个对象,由Kubernetes自己来进行管理和分配地址,当然我们也无法ping这个地址,他没有一个真正的实体对象来响应,他只能结合Service Port来组成一个可以通信的服务。
Service 类型
在定义Service的时候可以指定一个自己需要的类型的Service,如果不指定的话默认是ClusterIP类型。
可以使用的服务类型如下:
1、ClusterIP:通过集群的内部 IP 暴露服务,选择该值,服务只能够在集群内部可以访问,这也是默认的ServiceType。
2、NodePort:通过每个 Node 节点上的 IP 和静态端口(NodePort)暴露服务。NodePort 服务会路由到 ClusterIP 服务,这个 ClusterIP 服务会自动创建。通过请求 :,可以从集群的外部访问一个 NodePort 服务。
type 的值为 "NodePort",Kubernetes master 将从给定的配置范围内(默认:30000-32767)分配端口,每个 Node 将从该端口(每个 Node 上的同一端口)代理到 Service。该端口将通过 Service 的 spec.ports[*].nodePort 字段被指定,如果不指定的话会自动生成一个端口。
需要注意的是,Service 将能够通过 :spec.ports[].nodePort 和 spec.clusterIp:spec.ports[].port 而对外可见。
3、LoadBalancer:使用云提供商的负载局衡器,可以向外部暴露服务。外部的负载均衡器可以路由到 NodePort 服务和 ClusterIP 服务,这个需要结合具体的云厂商进行操作。
4、ExternalName:通过返回 CNAME 和它的值,可以将服务映射到 externalName 字段的内容(例如, foo.bar.example.com)。没有任何类型代理被创建,这只有 Kubernetes 1.7 或更高版本的 kube-dns 才支持。
Statefulset
RC、Deployment、DaemonSet都是面向无状态的服务,它们所管理的Pod的IP、名字,启停顺序等都是随机的,而StatefulSet是什么?顾名思义,有状态的集合,管理所有有状态的服务,比如MySQL、MongoDB集群等。
StatefulSet本质上是Deployment的一种变体,在v1.9版本中已成为GA版本,它为了解决有状态服务的问题,它所管理的Pod拥有固定的Pod名称,启停顺序,在StatefulSet中,Pod名字称为网络标识(hostname),还必须要用到共享存储。
除此之外,StatefulSet在Headless Service的基础上又为StatefulSet控制的每个Pod副本创建了一个DNS域名,这个域名的格式为:
$(podname).(headless server name)
FQDN: $(podname).(headless server name).namespace.svc.cluster.local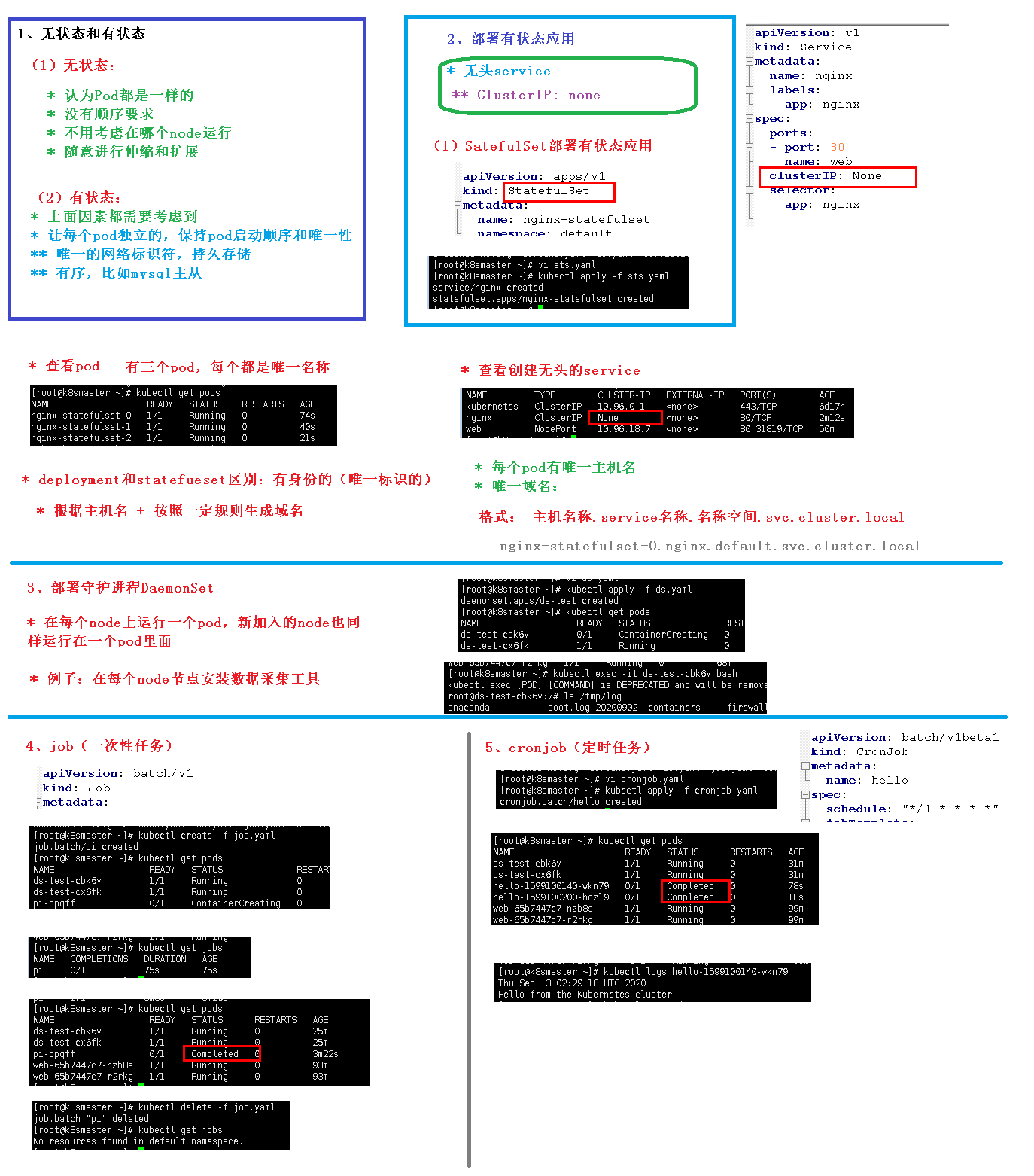
StatefulSet示例
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: web
clusterIP: None
selector:
app: nginx
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet
metadata:
name: web
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx # has to match .spec.template.metadata.labels
serviceName: "nginx" #声明它属于哪个Headless Service.
replicas: 3 # by default is 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx # has to match .spec.selector.matchLabels
spec:
terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10
containers:
- name: nginx
image: k8s.gcr.io/nginx-slim:0.8
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: web
volumeMounts:
- name: www
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
volumeClaimTemplates: #可看作pvc的模板
- metadata:
name: www
spec:
accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ]
storageClassName: "gluster-heketi" #存储类名,改为集群中已存在的
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi通过该配置文件,可看出StatefulSet的三个组成部分:
Headless Service:名为nginx,用来定义Pod网络标识( DNS domain)。StatefulSet:定义具体应用,名为Nginx,有三个Pod副本,并为每个Pod定义了一个域名。volumeClaimTemplates: 存储卷申请模板,创建PVC,指定pvc名称大小,将自动创建pvc,且pvc必须由存储类供应。
为什么需要 headless service 无头服务?
在用Deployment时,每一个Pod名称是没有顺序的,是随机字符串,因此是Pod名称是无序的,但是在statefulset中要求必须是有序 ,每一个pod不能被随意取代,pod重建后pod名称还是一样的。而pod IP是变化的,所以是以Pod名称来识别。pod名称是pod唯一性的标识符,必须持久稳定有效。这时候要用到无头服务,它可以给每个Pod一个唯一的名称 。
为什么需要volumeClaimTemplate?
对于有状态的副本集都会用到持久存储,对于分布式系统来讲,它的最大特点是数据是不一样的,所以各个节点不能使用同一存储卷,每个节点有自已的专用存储,但是如果在Deployment中的Pod template里定义的存储卷,是所有副本集共用一个存储卷,数据是相同的,因为是基于模板来的 ,而statefulset中每个Pod都要自已的专有存储卷,所以statefulset的存储卷就不能再用Pod模板来创建了,于是statefulSet使用volumeClaimTemplate,称为卷申请模板,它会为每个Pod生成不同的pvc,并绑定pv, 从而实现各pod有专用存储。这就是为什么要用volumeClaimTemplate的原因。
创建:
$ kubectl create -f nginx.yaml
service "nginx" created
statefulset "web" created看下这三个Pod创建过程:
#第一个是创建web-0
$ kubectl get pod
web-0 1/1 ContainerCreating 0 51s
#待web-0 running且ready时,创建web-1
$ kubectl get pod
web-0 1/1 Running 0 51s
web-1 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 42s
#待web-1 running且ready时,创建web-2
$ kubectl get pod
web-0 1/1 Running 0 1m
web-1 1/1 Running 0 45s
web-2 1/1 ContainerCreating 0 36s
#最后三个Pod全部running且ready
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
web-0 1/1 Running 0 4m
web-1 1/1 Running 0 3m
web-2 1/1 Running 0 1m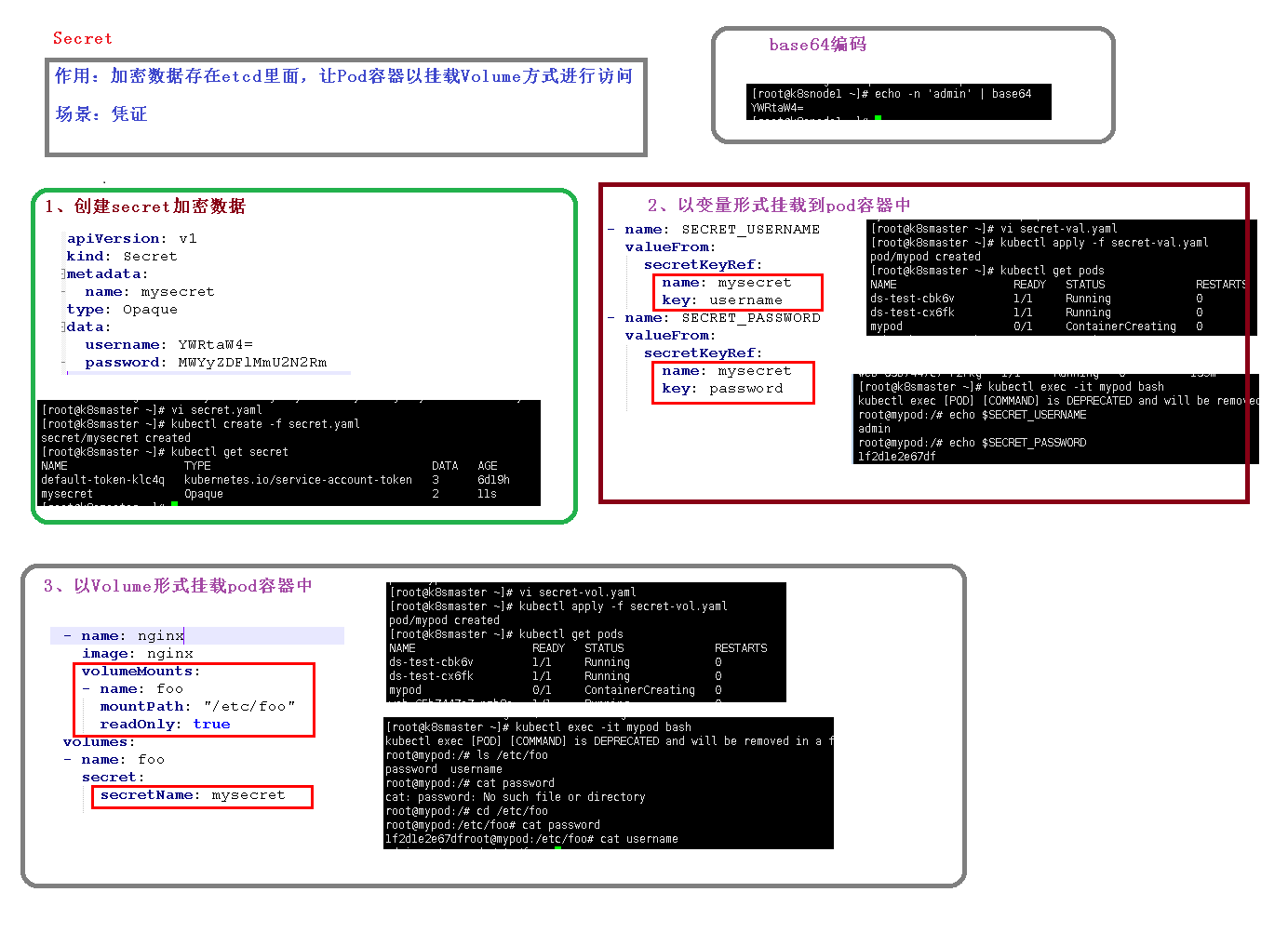
# 以变量形式挂载 创建secret.yaml
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]#touch secrt.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mysecret
type: Opaque
data:
username: zzzz
password: zzzz
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# kubectl create -f secrt.yaml
secret/mysecret created
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# kubectl get secret
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
default-token-5rv5r kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 3d19h
mysecret Opaque 2 10s
sh.helm.release.v1.web1.v1 helm.sh/release.v1 1 2d21h
sh.helm.release.v1.web1.v2 helm.sh/release.v1 1 2d21h
sh.helm.release.v1.web2.v1 helm.sh/release.v1 1 2d20h
sh.helm.release.v1.web3.v1 helm.sh/release.v1 1 2d20h
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# cat secrt-var.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
env:
- name: SECRET_USERNAME
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysecret
key: username
- name: SECRET_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: mysecret
key: password
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# kubectl create -f secrt-var.yaml
pod/mypod created
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
mypod 1/1 Running 0 10s
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# kubectl describe pod mypod
Name: mypod
Namespace: default
Priority: 0
Node: k8s-node2/192.168.44.4
Start Time: Fri, 25 Sep 2020 17:26:21 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: 10.244.1.26
IPs:
IP: 10.244.1.26
Containers:
nginx:
Container ID: docker://a8cbca4f3d6fdc2e6045419aeb529b77828c2aaa6895ebc8373705b4d6850d03
Image: nginx
Image ID: docker-pullable://nginx@sha256:c628b67d21744fce822d22fdcc0389f6bd763daac23a6b77147d0712ea7102d0
Port: <none>
Host Port: <none>
State: Running
Started: Fri, 25 Sep 2020 17:26:25 +0800
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Environment:
SECRET_USERNAME: <set to the key 'username' in secret 'mysecret'> Optional: false
SECRET_USERNAME: <set to the key 'password' in secret 'mysecret'> Optional: false
Mounts:
/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount from default-token-5rv5r (ro)
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready True
ContainersReady True
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
default-token-5rv5r:
Type: Secret (a volume populated by a Secret)
SecretName: default-token-5rv5r
Optional: false
QoS Class: BestEffort
Node-Selectors: <none>
Tolerations: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
node.kubernetes.io/unreachable:NoExecute op=Exists for 300s
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal Scheduled 5m2s default-scheduler Successfully assigned default/mypod to k8s-node2
Normal Pulling 4m59s kubelet Pulling image "nginx"
Normal Pulled 4m56s kubelet Successfully pulled image "nginx"
Normal Created 4m56s kubelet Created container nginx
Normal Started 4m56s kubelet Started container nginx
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# kubectl exec -it mypod bash
kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead.
error: unable to upgrade connection: container not found ("nginx")
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# kubectl exec -it mypod bash
kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead.
root@mypod:/# echo $SECRET_PASSWORD
�<�
root@mypod:/# echo $SECRET_USERNAME
�<�
# 以数据卷挂载
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# kubectl create -f secrt-vol.yaml
pod/mypod created
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# cat secrt-vol.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: foo
mountPath: "/etc/foo"
volumes:
- name: foo
secret:
secretName: mysecret
[root@k8s-master k8s-secret]# kubectl exec -it mypod bash
kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead.
root@mypod:/# cd /etc/foo
root@mypod:/etc/foo# ls
password username
root@mypod:/etc/foo# cat password
▒<▒root@mypod:/etc/foo# cat username
▒<▒root@mypod:/etc/foo#
root@mypod:/etc/foo# echo -n 'aaa'|base64
YWFh
ConfigMap
ConfigMap顾名思义,是用于保存配置数据的键值对,可以用来保存单个属性,也可以保存配置文件。Secret可以为Pod提供密码、Token、私钥等敏感数据;对于一些非敏感数据,比如应用的配置信息,则可以使用ConfigMap。
ConfigMap的创建和使用方式与Secret非常类似,主要的不同是以明文的形式存放。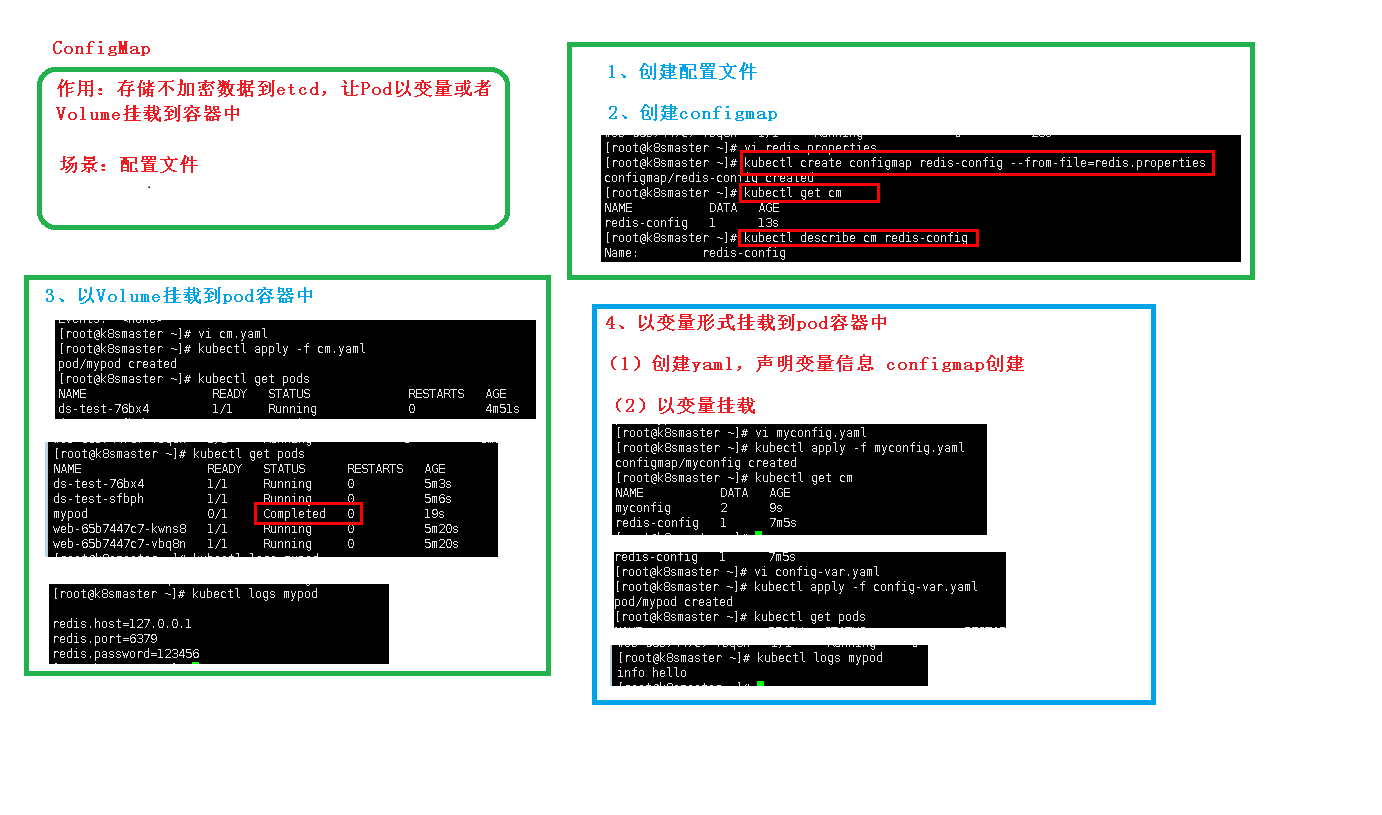
[root@k8s-master config]# vi redis.props
[root@k8s-master config]# kubectl create configmap redis-config --from-file=redis.props
configmap/redis-config created
[root@k8s-master config]# ls
redis.props
[root@k8s-master config]# kubectl get cm
NAME DATA AGE
redis-config 1 18s
[root@k8s-master config]# kubectl describe cm redis-config
Name: redis-config
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Data
====
redis.props:
----
redis.host=127.0.0.1
redis.port=6379
redis.password=123456
Events: <none>
[root@k8s-master config]# cat redis.props
redis.host=127.0.0.1
redis.port=6379
redis.password=123456
# 以数据卷挂载
[root@k8s-master config]# cat cm.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
containers:
- name: busybox
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","cat /etc/config/redis.props"]
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/config
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: redis-config
restartPolicy: Never
[root@k8s-master config]# kubectl apply -f cm.yaml
[root@k8s-master config]# kubectl logs mypod
redis.host=127.0.0.1
redis.port=6379
redis.password=123456
# 以变量挂载
[root@k8s-master config]# vi var.yaml
[root@k8s-master config]# cat var.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: myconfig
namespace: default
data:
special.level: info
special.type: hello
[root@k8s-master config]# kubectl apply -f var.yaml
configmap/myconfig created
[root@k8s-master config]# kubectl get cm
NAME DATA AGE
myconfig 2 8s
redis-config 1 19m
[root@k8s-master config]# cat con-var.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: mypod
spec:
containers:
- name: busybox
image: busybox
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","echo $(LEVEL) $(TYPE)"]
env:
- name: LEVEL
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: myconfig
key: special.level
- name: TYPE
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: myconfig
key: special.type
restartPolicy: Never
[root@k8s-master config]# kubectl apply -f con-var.yaml
pod/mypod created
[root@k8s-master config]# kubectl get cm
NAME DATA AGE
myconfig 2 25m
redis-config 1 44m
[root@k8s-master config]# kubectl logs mypod
info hello
ConfigMap的创建
可以使用 kubectl create configmap 从文件、目录或者 key-value 字符串创建等创建 ConfigMap。也可以通过 kubectl create -f从描述文件创建。
从key-value字符串创建
$ kubectl create configmap special-config --from-literal=special.how=very
configmap "special-config" created
$ kubectl get configmap special-config -o go-template='{{.data}}'
map[special.how:very]上面的命令创建了一个名为special-config,拥有一条key为special.how,value为very的键值对数据。
从env文件创建
$ echo -e "a=b\nc=d" | tee config.env
a=b
c=d
$ kubectl create configmap special-config --from-env-file=config.env
configmap "special-config" created
$ kubectl get configmap special-config -o go-template='{{.data}}'
map[a:b c:d]上面的命令从一个env文件读取键值对,然后存入一个名为special-config的ConfigMap中。
从目录创建
$ mkdir config
$ echo a>config/a
$ echo b>config/b
$ kubectl create configmap special-config --from-file=config/
configmap "special-config" created
$ kubectl get configmap special-config -o go-template='{{.data}}'
map[a:a
b:b
]上面的命令读取config目录下的所有文件,以文件名为key,文件内容为value,存入名为special-config的ConfigMap中。
根据yaml描述文件创建
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: special-config
data:
special.how: very
special.type: charm$ kubectl create -f config.yaml
configmap "special-config" createdConfigMap的使用
Pod可以通过三种方式来使用ConfigMap,分别为:
- 将ConfigMap中的数据设置为环境变量
- 将ConfigMap中的数据设置为命令行参数
- 使用Volume将ConfigMap作为文件或目录挂载
注意!!
- ConfigMap必须在Pod使用它之前创建
- 使用envFrom时,将会自动忽略无效的键
- Pod只能使用同一个命名空间的ConfigMap
用作环境变量
首先创建两个ConfigMap,分别名为special-config和env-config:
$ kubectl create configmap special-config --from-literal=special.how=very --from-literal=special.type=charm
$ kubectl create configmap env-config --from-literal=log_level=INFO然后以环境变量方式引用:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: test-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: test-container
image: gcr.io/google_containers/busybox
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "env" ]
env:
- name: SPECIAL_LEVEL_KEY
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: special-config
key: special.how
- name: SPECIAL_TYPE_KEY
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: special-config
key: special.type
envFrom:
- configMapRef:
name: env-config
restartPolicy: Never当pod运行结束后,它的输出如下:
SPECIAL_LEVEL_KEY=very
SPECIAL_TYPE_KEY=charm
log_level=INFO用作命令行参数
将ConfigMap用作命令行参数时,需要先把ConfigMap的数据保存在环境变量中,然后通过$(VAR_NAME)的方式引用环境变量。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: dapi-test-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: test-container
image: gcr.io/google_containers/busybox
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "echo $(SPECIAL_LEVEL_KEY) $(SPECIAL_TYPE_KEY)" ]
env:
- name: SPECIAL_LEVEL_KEY
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: special-config
key: special.how
- name: SPECIAL_TYPE_KEY
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: special-config
key: special.type
restartPolicy: Never当pod运行结束后,它的输出如下:
very charm使用volume将ConfigMap作为文件或目录直接挂载
将创建的ConfigMap直接挂载至Pod的/etc/config目录下,其中每一个key-value键值对都会生成一个文件,key为文件名,value为内容。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: vol-test-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: test-container
image: gcr.io/google_containers/busybox
command: [ "/bin/sh", "-c", "cat /etc/config/special.how" ]
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/config
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: special-config
restartPolicy: Never当Pod结束后会输出:
Never将创建的ConfigMap中special.how这个key挂载到/etc/config目录下的一个相对路径/keys/special.level。如果存在同名文件,直接覆盖。其他的key不挂载。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: dapi-test-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: test-container
image: gcr.io/google_containers/busybox
command: [ "/bin/sh","-c","cat /etc/config/keys/special.level" ]
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/config
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: special-config
items:
- key: special.how
path: keys/special.level
restartPolicy: Never当Pod结束后会输出:
Never在一般情况下 configmap 挂载文件时,会先覆盖掉挂载目录,然后再将 congfigmap 中的内容作为文件挂载进行。如果想不对原来的文件夹下的文件造成覆盖,只是将 configmap 中的每个 key,按照文件的方式挂载到目录下,可以使用 subpath 参数。
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: dapi-test-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: test-container
image: nginx
command: ["/bin/sh","-c","sleep 36000"]
volumeMounts:
- name: config-volume
mountPath: /etc/nginx/special.how
subPath: special.how
volumes:
- name: config-volume
configMap:
name: special-config
items:
- key: special.how
path: special.how
restartPolicy: Neverroot@dapi-test-pod:/# ls /etc/nginx/
conf.d fastcgi_params koi-utf koi-win mime.types modules nginx.conf scgi_params special.how uwsgi_params win-utf
root@dapi-test-pod:/# cat /etc/nginx/special.how
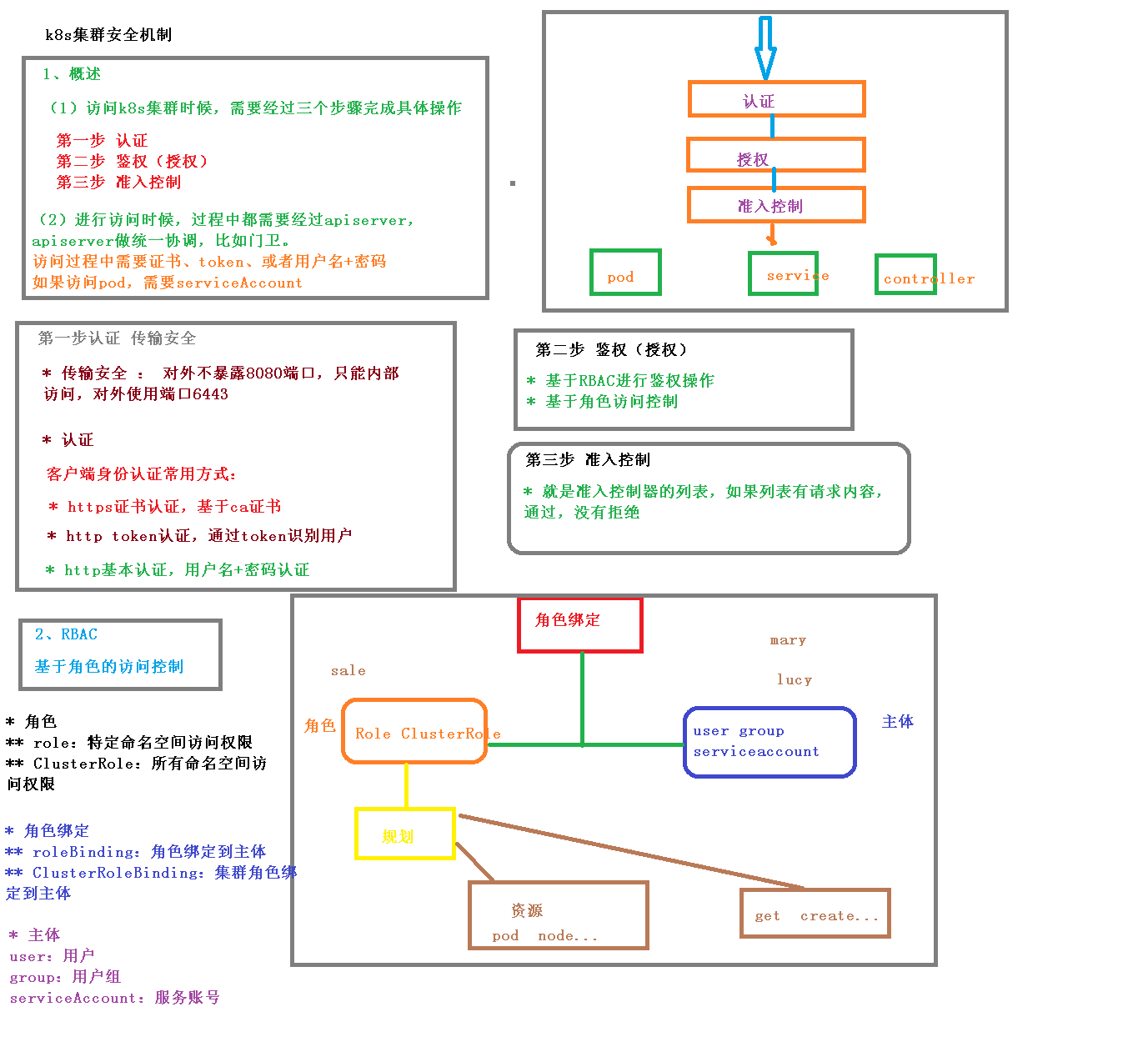
Never集群安全机制
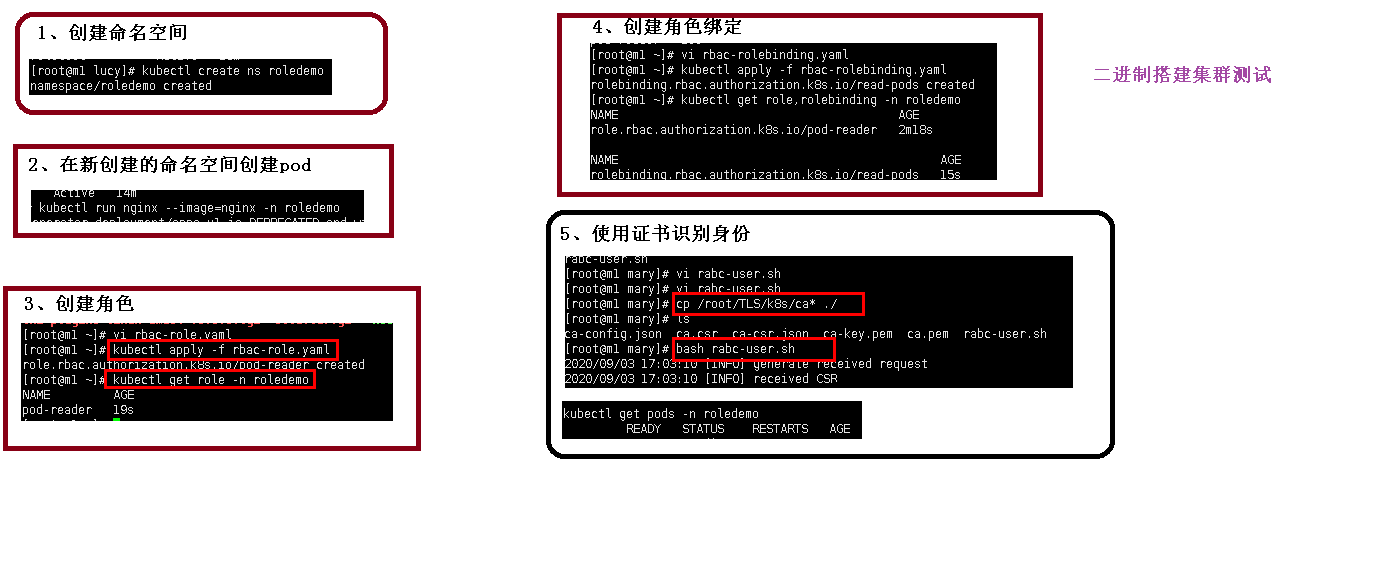
# 1.0 创建命名空间
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 17h
kube-node-lease Active 17h
kube-public Active 17h
kube-system Active 17h
nstest Active 3h20m
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl create ns roledemo
namespace/roledemo created
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get ns
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 17h
kube-node-lease Active 17h
kube-public Active 17h
kube-system Active 17h
nstest Active 3h20m
roledemo Active 3s
#2.0 在新创建的命名空间里创建pod
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl run nginx --image=nginx -n roledemo
pod/nginx created
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods -n roledemo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx 1/1 Running 0 31s
#3.0 创建角色
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat rbac-role.yaml
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: roledemo
name: pod-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # "" indicates the core API group
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f rbac-role.yaml
role.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/pod-reader created
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get role -n roledemo
NAME CREATED AT
pod-reader 2020-09-22T07:11:01Z
# 创建角色绑定
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat rbac-rolebing.yaml
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: read-pods
namespace: roledemo
subjects:
- kind: User
name: lucy # Name is case sensitive
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: Role #this must be Role or ClusterRole
name: pod-reader # this must match the name of the Role or ClusterRole you wish to bind to
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f rbac-rolebing.yaml
rolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/read-pods created
# 使用证书识别
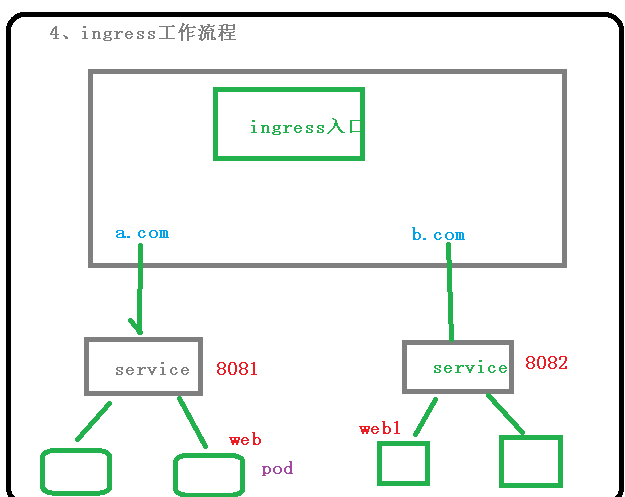
ingress
把端口对外暴露,通过ip+端口进行访问
- 使用Service里面的NodePort实现
NodePort缺陷
- 每个节点都有端口,在访问时候通过任何节点通过节点ip+port实现访问
- 意味着每个端口使用一次,一个端口对应一个应用
实际应用中使用域名,根据不同域名跳转到不同端口
Ingress和Pod关系
- pod和ingress通过service关联
- ingress作为统一入口,由service关联一组pod
使用ingress
- 部署ingress controller
- 创建ingress规则
这里选择nginx控制器实现部署
使用ingress对外暴露应用
1 创建nginx应用,暴露端口使用NodePort
[root@k8s-master mary]# kubectl create deployment web --image=nginx
deployment.apps/web created
[root@k8s-master mary]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
web-5dcb957ccc-jfcr7 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 11s
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl expose deployment web --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=NodePort
service/web exposed
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 19h
web NodePort 10.100.245.172 <none> 80:31909/TCP 9s
2 部署ingress controller
kubectl apply -f ingress-controller.yaml
查看ingress状态
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl apply -f ingress-h.yaml
ingress.networking.k8s.io/example-ingress created
[root@k8s-master ~]# cat ingress-h.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: example-ingress
spec:
rules:
- host: example.ingredemo.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: web
servicePort: 80
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-ingress-controller-766fb9f77-6tvzw 0/1 ContainerCreating 0
[root@k8s-master ~]# kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
nginx-ingress-controller-766fb9f77-6tvzw 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 5m28s 192.168.44.4 k8s-node2 <none> <none>
3 在windows系统hosts文件中添加域名访问规则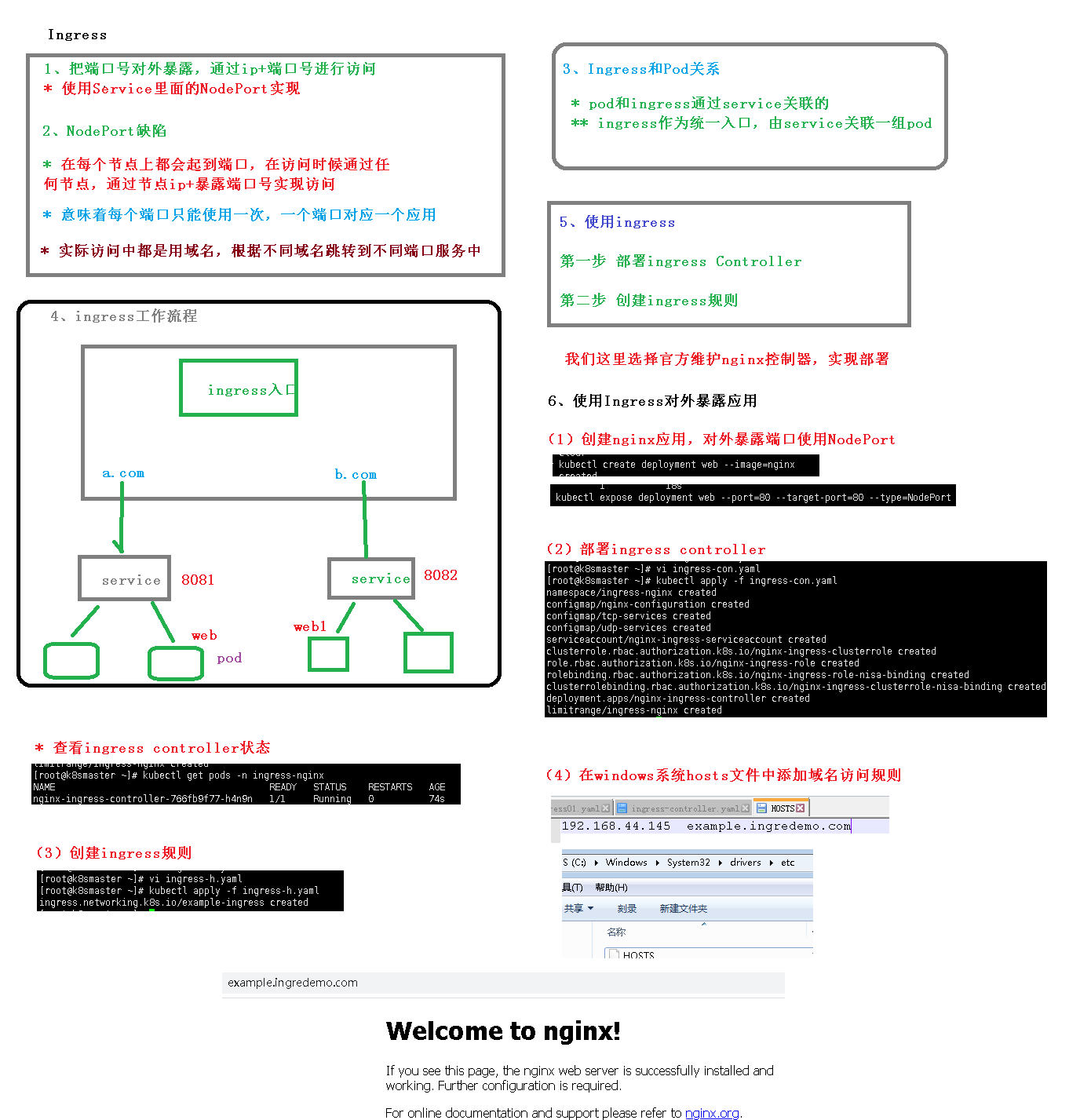
Helm
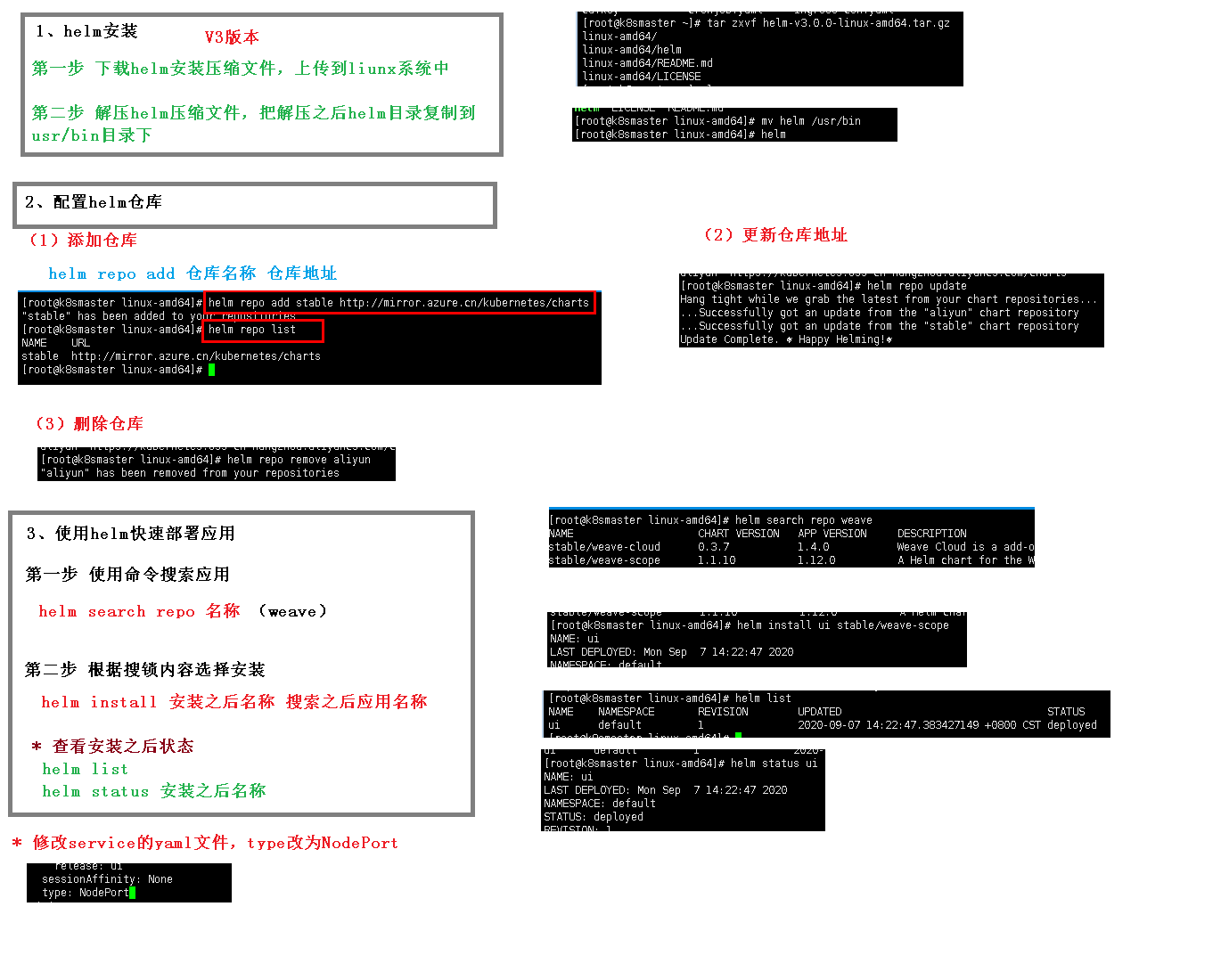
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# helm search repo weace
No results found
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# helm search repo weave
NAME CHART VERSION APP VERSION DESCRIPTION
aliyun/weave-cloud 0.1.2 Weave Cloud is a add-on to Kubernetes which pro...
aliyun/weave-scope 0.9.2 1.6.5 A Helm chart for the Weave Scope cluster visual...
stable/weave-cloud 0.3.7 1.4.0 Weave Cloud is a add-on to Kubernetes which pro...
stable/weave-scope 1.1.10 1.12.0 A Helm chart for the Weave Scope cluster visual...
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# helm install ui stable/weave-cloud
Error: unable to build kubernetes objects from release manifest: error validating "": error validating data: unknown object type "nil" in Secret.data.token
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# helm install ui stable/weave-scope
NAME: ui
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Sep 22 17:48:42 2020
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
NOTES:
You should now be able to access the Scope frontend in your web browser, by
using kubectl port-forward:
kubectl -n default port-forward $(kubectl -n default get endpoints \
ui-weave-scope -o jsonpath='{.subsets[0].addresses[0].targetRef.name}') 8080:4040
then browsing to http://localhost:8080/.
For more details on using Weave Scope, see the Weave Scope documentation:
https://www.weave.works/docs/scope/latest/introducing/

[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# helm create mychart
Creating mychart
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# ls
LICENSE mychart README.md
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# cd mychart/
[root@k8s-master mychart]# ls
charts Chart.yaml templates values.yaml
[root@k8s-master mychart]# ls charts/
[root@k8s-master mychart]# cat Chart.yaml
apiVersion: v2
name: mychart
description: A Helm chart for Kubernetes
# A chart can be either an 'application' or a 'library' chart.
#
# Application charts are a collection of templates that can be packaged into versioned archives
# to be deployed.
#
# Library charts provide useful utilities or functions for the chart developer. They're include
# a dependency of application charts to inject those utilities and functions into the rendering
# pipeline. Library charts do not define any templates and therefore cannot be deployed.
type: application
# This is the chart version. This version number should be incremented each time you make chang
# to the chart and its templates, including the app version.
# Versions are expected to follow Semantic Versioning (https://semver.org/)
version: 0.1.0
# This is the version number of the application being deployed. This version number should be
# incremented each time you make changes to the application. Versions are not expected to
# follow Semantic Versioning. They should reflect the version the application is using.
appVersion: 1.16.0
[root@k8s-master mychart]# cd templates/
[root@k8s-master templates]# ls
deployment.yaml _helpers.tpl hpa.yaml ingress.yaml NOTES.txt serviceaccount.yaml service.
[root@k8s-master templates]# rm -rf *
[root@k8s-master templates]# kubectl create deployment web1 --image=nginx --dry-run -o yaml > deployment.yaml
W0922 18:04:32.306200 114013 helpers.go:553] --dry-run is deprecated and can be replaced with --dry-run=client.
[root@k8s-master templates]# ls
deployment.yaml
[root@k8s-master templates]# kubectl expose deployment web1 --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=NodePort --dry-run -o yaml > service.yaml
W0922 19:32:20.372410 51616 helpers.go:553] --dry-run is deprecated and can be replaced with --dry-run=client.
Error from server (NotFound): deployments.apps "web1" not found
[root@k8s-master templates]# ^C
[root@k8s-master templates]# kubectl create deployment web1 --image=nginx
deployment.apps/web1 created
[root@k8s-master templates]# kubectl expose deployment web1 --port=80 --target-port=80 --type=NodePort --dry-run -o yaml > service.yaml
W0922 19:33:56.819969 52907 helpers.go:553] --dry-run is deprecated and can be replaced with --dry-run=client.
[root@k8s-master templates]# ls
deployment.yaml service.yaml
[root@k8s-master templates]# vi service.yaml
[root@k8s-master templates]# cd ..
[root@k8s-master mychart]# ls
charts Chart.yaml templates values.yaml
[root@k8s-master mychart]# cd ..
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl delete deployment web1
deployment.apps "web1" deleted
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# helm install web1 mychart/
NAME: web1
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Sep 22 19:36:47 2020
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
web1-7f87dfbd56-xpdnp 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 6s
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
web1-7f87dfbd56-xpdnp 1/1 Running 0 10s
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# helm upgrade web1 mychart/
Release "web1" has been upgraded. Happy Helming!
NAME: web1
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Sep 22 19:37:41 2020
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 2
TEST SUITE: None
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# cd mychart/
[root@k8s-master mychart]# ls
charts Chart.yaml templates values.yaml
[root@k8s-master mychart]# vi values.yaml
[root@k8s-master mychart]# vi templates/
[root@k8s-master mychart]# ls
charts Chart.yaml templates values.yaml
[root@k8s-master mychart]# cd templates/
[root@k8s-master templates]# ls
deployment.yaml service.yaml
[root@k8s-master templates]# vi deployment.yaml
[root@k8s-master templates]# vi service.yaml
[root@k8s-master templates]# cd ..
[root@k8s-master mychart]# cd ..
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# ls
LICENSE mychart README.md
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# helm install --dry-run web2 mychart/
NAME: web2
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Sep 22 20:04:53 2020
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: pending-install
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
HOOKS:
MANIFEST:
---
# Source: mychart/templates/service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: web2.svc
name: web2.svc
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx
type: NodePort
status:
loadBalancer: {}
---
# Source: mychart/templates/deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: web2.deploy
name: web2.deploy
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
strategy: {}
template:
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: nginx
name: nginx
resources: {}
status: {}
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# helm install web2 mychart/
Error: Service "web2.svc" is invalid: metadata.name: Invalid value: "web2.svc": a DNS-1035 label must consist of lower case alphanumeric characters or '-', start with an alphabetic character, and end with an alphanumeric character (e.g. 'my-name', or 'abc-123', regex used for validation is '[a-z]([-a-z0-9]*[a-z0-9])?')
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# cd mychart/
[root@k8s-master mychart]# cd templates/
[root@k8s-master templates]# ls
deployment.yaml service.yaml
[root@k8s-master templates]# vi service.yaml
[root@k8s-master templates]# vi deployment.yaml
[root@k8s-master templates]# cd ..
[root@k8s-master mychart]# cd ..
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# helm install web3 mychart/
NAME: web3
LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Sep 22 20:07:48 2020
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
web1-7f87dfbd56-xpdnp 1/1 Running 0 31m
web2.deploy-f89759699-4zt7v 1/1 Running 0 2m22s
web3-deploy-f89759699-whsfl 1/1 Running 0 31s
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl delete deployment web1-7f87dfbd56-xpdnp
Error from server (NotFound): deployments.apps "web1-7f87dfbd56-xpdnp" not found
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
web1 1/1 1 1 32m
web2.deploy 1/1 1 1 3m19s
web3-deploy 1/1 1 1 89s
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl delete deployment web1
deployment.apps "web1" deleted
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl delete deployment web2.deploy
deployment.apps "web2.deploy" deleted
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl get deployment
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
web3-deploy 1/1 1 1 105s
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
web2.deploy-f89759699-4zt7v 0/1 Terminating 0 3m43s
web3-deploy-f89759699-whsfl 1/1 Running 0 112s
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
web3-deploy-f89759699-whsfl 1/1 Running 0 116s
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 23h
web NodePort 10.100.245.172 <none> 80:31909/TCP 3h49m
web1 NodePort 10.101.250.39 <none> 80:31918/TCP 33m
web3-svc NodePort 10.108.54.39 <none> 80:30510/TCP 2m14s
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl delete svc web
service "web" deleted
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl delete svc web1
service "web1" deleted
[root@k8s-master linux-amd64]# kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 23h
web3-svc NodePort 10.108.54.39 <none> 80:30510/TCP 2m35s
持久化存储
nfs,网络存储 pod重启,数据还在
1 找一台服务器nfs服务器
安装nfs
[root@nfs nfs]# yum install -y nfs-utils
设置挂载路径
[root@nfs nfs]# vi /etc/exports
挂载路径创建
[root@nfs data]# mkdir nfs
2 在k8s集群节点安装nfs
[root@k8s-node]# yum install -y nfs-utils
3 在nfs服务器上启动nfs服务
[root@nfs nfs]# systemctl start nfs
[root@nfs nfs]# ps -ef | grep nfs
root 8974 2 0 20:52 ? 00:00:00 [nfsd4_callbacks]
root 8980 2 0 20:52 ? 00:00:00 [nfsd]
root 8981 2 0 20:52 ? 00:00:00 [nfsd]
root 8982 2 0 20:52 ? 00:00:00 [nfsd]
root 8983 2 0 20:52 ? 00:00:00 [nfsd]
root 8984 2 0 20:52 ? 00:00:00 [nfsd]
root 8985 2 0 20:52 ? 00:00:00 [nfsd]
root 8986 2 0 20:52 ? 00:00:00 [nfsd]
root 8987 2 0 20:52 ? 00:00:00 [nfsd]
root 11057 2 0 20:56 ? 00:00:00 [nfsiod]
root 15624 2 0 21:05 ? 00:00:00 [nfsv4.
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl apply -f nfs-nginx.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx-dep1 created
4 在k8s集群部署使用nfs持久化存储
[root@k8s-master pv]# cat nfs-nginx.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-dep1
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: wwwroot
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumes:
- name: wwwroot
nfs:
server: 192.168.44.6
path: /data/nfs
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl apply -f nfs-nginx.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx-dep1 created
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl exec -it nginx-dep1-84468dfbc6-gfjnp bash
kubectl exec [POD] [COMMAND] is DEPRECATED and will be removed in a future version. Use kubectl exec [POD] -- [COMMAND] instead.
root@nginx-dep1-84468dfbc6-gfjnp:/# ls /usr/share/nginx/html
root@nginx-dep1-84468dfbc6-gfjnp:/# ls
bin docker-entrypoint.d home media proc sbin tmp
boot docker-entrypoint.sh lib mnt root srv usr
dev etc lib64 opt run sys var
root@nginx-dep1-84468dfbc6-gfjnp:/# ls /usr/share/nginx/html
hello.html
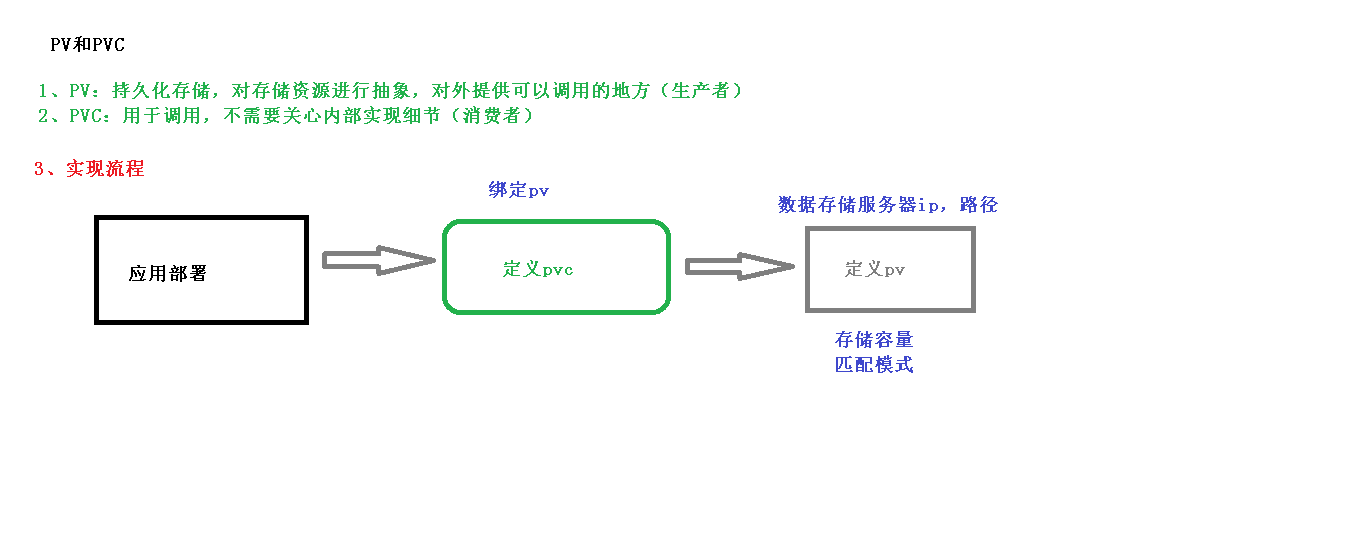
pv pvc
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl apply -f pvc.yaml
deployment.apps/nginx-dep1 created
persistentvolumeclaim/my-pvc created
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-dep1-58b7bf955f-n57mk 0/1 Pending 0 15s
nginx-dep1-58b7bf955f-tktq4 0/1 Pending 0 15s
nginx-dep1-58b7bf955f-x4zwj 0/1 Pending 0 15s
[root@k8s-master pv]# cat pvc.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-dep1
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
volumeMounts:
- name: wwwroot
mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumes:
- name: wwwroot
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: my-pvc
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
metadata:
name: my-pvc
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
resources:
requests:
storage: 5Gi[root@k8s-master pv]#
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl apply -f pv.yaml
persistentvolume/my-pv created
[root@k8s-master pv]# cat pv.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: my-pv
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteMany
nfs:
path: /data/nfs
server: 192.168.44.6
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl get pv,pvc
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
persistentvolume/my-pv 5Gi RWX Retain Bound default/my-pvc 6s
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
persistentvolumeclaim/my-pvc Bound my-pv 5Gi RWX 100s
[root@k8s-master pv]# kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-dep1-58b7bf955f-n57mk 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2m3s
nginx-dep1-58b7bf955f-tktq4 1/1 Running 0 2m3s
nginx-dep1-58b7bf955f-x4zwj 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2m3s
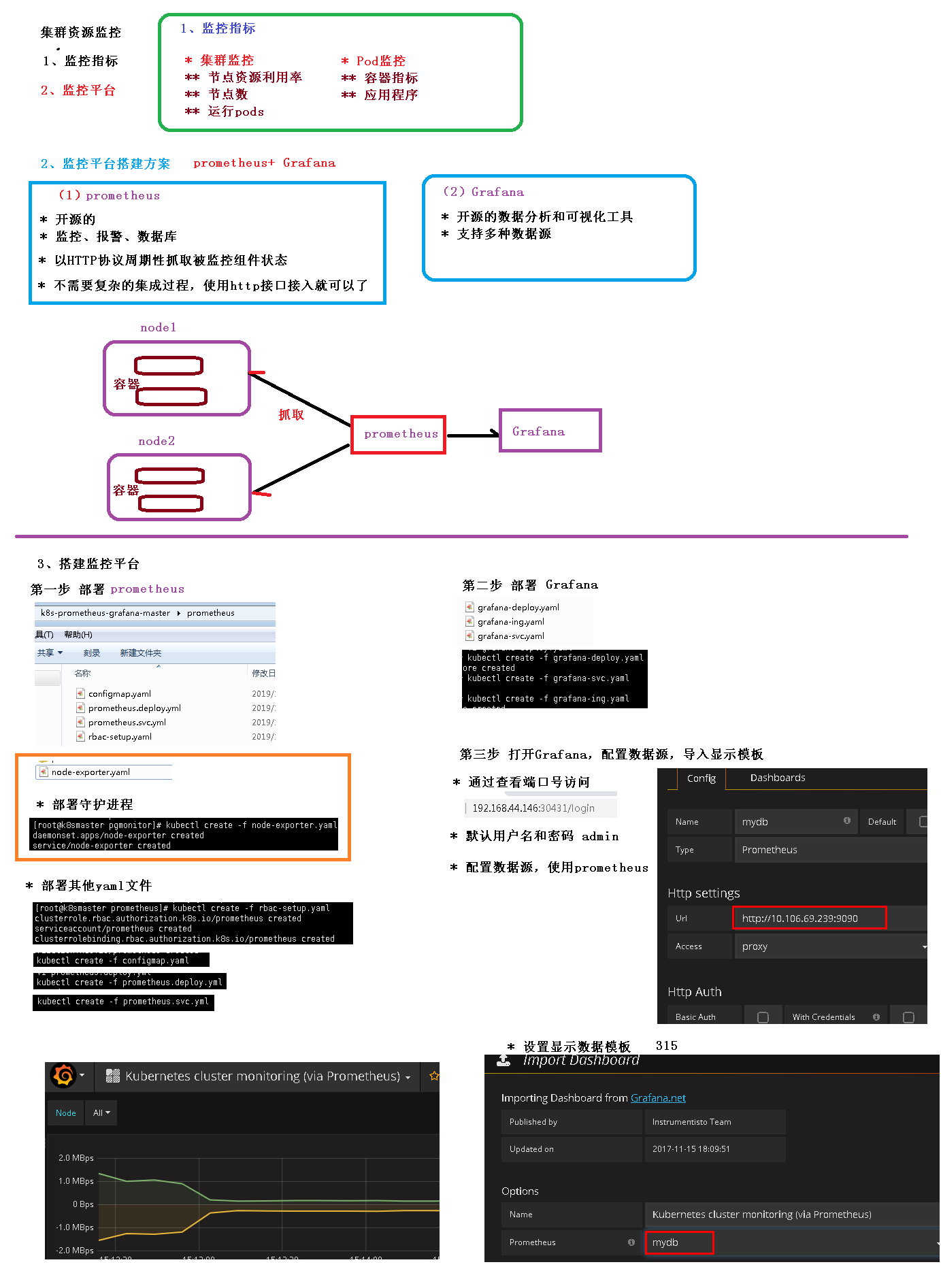
集群资源监控
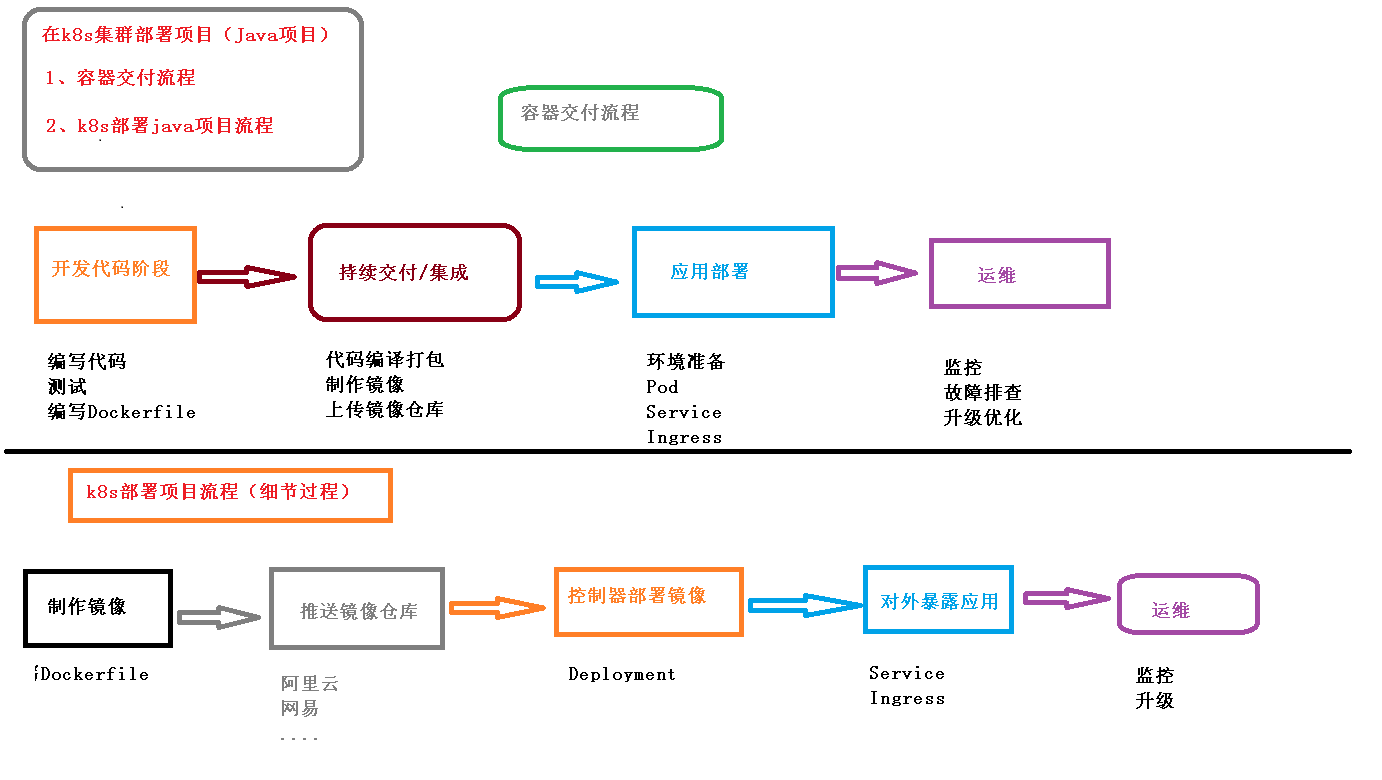
常见问题
删除pod
当创建此pod时,kubernetes会同时创建一个副本控制器,用以监控此yaml文件创建对象的状态,当检测到异常时,会自动创建一个,故,不管我们怎么删都删不掉。
至此,我们可以总结出,当kubectl delete操作无效时可以尝试下面几个步骤来排查原因:
- 检查是否创建了deployments任务:
kubectl get deployments - 检查是否创建了副本控制器ReplicationController:
kubectl get rc - 检查是否创建了副本集replicasets:
kubectl get rs
如果有,先执行kubectl delete deployment|rc|rs $name后在执行kubectl delete pod $pod_name方可真正实现删除目的。
kubectl create 和 kubectl apply区别
- 描述:
kubectl create -f xx.yaml
kubectl apply -f xx.yaml
如果yaml文件中的kind值为deployment,那么上面这两个命令都可以创建一个deployment,生成相应数量的pod
那二者有什么区别呢?
- 区别:
kubectl create:
(1)kubectl create命令,是先删除所有现有的东西,重新根据yaml文件生成新的。所以要求yaml文件中的配置必须是完整的
(2)kubectl create命令,用同一个yaml 文件执行替换replace命令,将会不成功,fail掉。
kubectl apply:
kubectl apply命令,根据配置文件里面列出来的内容,升级现有的。所以yaml文件的内容可以只写需要升级的属性
列举出 Deployment 创建的 pods:
kubectl get pods -l app=mysql| 关键字 | 是否必须 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| image | 否 | 用于docker镜像,查看docker文档 |
| services | 否 | 用于docker服务,查看docker文档 |
| stages | 否 | 定义构建阶段 |
| types | 否 | stages 的别名(已废除) |
| before_script | 否 | 定义在每个job之前运行的命令 |
| after_script | 否 | 定义在每个job之后运行的命令 |
| variable | 否 | 定义构建变量 |
| cache | 否 | 定义一组文件列表,可在后续运行中使用 |

新盘新项目,不再等待,现在就是最佳上车机会!
2025年10月新盘 做第一批吃螃蟹的人coinsrore.com
新车新盘 嘎嘎稳 嘎嘎靠谱coinsrore.com
新车首发,新的一年,只带想赚米的人coinsrore.com
新盘 上车集合 留下 我要发发 立马进裙coinsrore.com
做了几十年的项目 我总结了最好的一个盘(纯干货)coinsrore.com
新车上路,只带前10个人coinsrore.com
新盘首开 新盘首开 征召客户!!!coinsrore.com
新项目准备上线,寻找志同道合的合作伙伴coinsrore.com
新车即将上线 真正的项目,期待你的参与coinsrore.com
新盘新项目,不再等待,现在就是最佳上车机会!coinsrore.com
新盘新盘 这个月刚上新盘 新车第一个吃螃蟹!coinsrore.com
2025年10月新盘 做第一批吃螃蟹的人coinsrore.com
新车新盘 嘎嘎稳 嘎嘎靠谱coinsrore.com
新车首发,新的一年,只带想赚米的人coinsrore.com
新盘 上车集合 留下 我要发发 立马进裙coinsrore.com
做了几十年的项目 我总结了最好的一个盘(纯干货)coinsrore.com
新车上路,只带前10个人coinsrore.com
新盘首开 新盘首开 征召客户!!!coinsrore.com
新项目准备上线,寻找志同道合 的合作伙伴coinsrore.com
新车即将上线 真正的项目,期待你的参与coinsrore.com
新盘新项目,不再等待,现在就是最佳上车机会!coinsrore.com
新盘新盘 这个月刚上新盘 新车第一个吃螃蟹!coinsrore.com
华纳东方明珠客服电话是多少?(▲18288362750?《?微信STS5099? 】
如何联系华纳东方明珠客服?(▲18288362750?《?微信STS5099? 】
华纳东方明珠官方客服联系方式?(▲18288362750?《?微信STS5099?
华纳东方明珠客服热线?(▲18288362750?《?微信STS5099?
华纳东方明珠24小时客服电话?(▲18288362750?《?微信STS5099? 】
华纳东方明珠官方客服在线咨询?(▲18288362750?《?微信STS5099?
《华纳圣淘沙公司开户流程全解析》→ 官方顾问一对一指导??? 安全联系:183第三段8890第四段9465
《华纳圣淘沙开户步骤详解》→ 」专属通道快速办理??? 安全联系:183第三段8890第四段9465
《华纳圣淘沙账户注册指南》→ 扫码获取完整资料清单?「微?? 安全联系:183第三段8890第四段9465
《新手开通华纳圣淘沙公司账户指南》→ 限时免费咨询开放??? 安全联系:183第三段8890第四段9465
《华纳圣淘沙企业开户标准流程》→ 资深顾问实时解答疑问??? 安全联系:183第三段8890第四段9465
《华纳圣淘沙开户步骤全景图》→ 点击获取极速开户方案??? 安全联系:183第三段8890第四段9465
《华纳圣淘沙账户创建全流程手册》→ 预约顾问免排队服务?9?? 安全联系:183第三段8890第四段9465 《从零开通华纳圣淘沙公司账户》→ 添加客服领取开户工具包?? 安全联系:183第三段8890第四段9465
《官方授权:华纳圣淘沙开户流程》→ 认证顾问全程代办?」?? 安全联系:183第三段8890第四段9465
《华纳圣淘沙开户说明书》→立即联系获取电子版文件??? 安全联系:183第三段8890第四段9465